Egypt, a land primarily defined by the mighty Nile and expansive deserts, also harbors a fascinating network of natural water bodies beyond its famous river. These lakes, often formed by geological depressions or connected to coastal systems, are vital for wildlife, local communities, and offer unique ecological insights into the region.
This guide presents a comprehensive overview of 17 Lakes in Egypt, ranging from the vast expanse of the Great Bitter Lake to the distinctive mineral-rich Wadi El Natrun Lakes. For each, you’ll find key details including its Location, Surface Area (km²), and a defining Key Feature, all organized for your convenience below.
What types of lakes are commonly found in Egypt?
Egypt features a diverse range of lakes. These include large coastal lagoons along the Mediterranean and Red Sea, which are often saline or brackish and support rich marine life. Inland, there are freshwater lakes connected to the Nile system, and perhaps most uniquely, hypersaline soda lakes found in desert depressions, such as those in Wadi El Natrun, which are characterized by extremely high mineral content and unique extremophile ecosystems.
Is Lake Nasser considered one of Egypt’s natural lakes?
While Lake Nasser is a colossal and immensely important body of water within Egypt, it is technically an artificial reservoir. It was created by the construction of the Aswan High Dam on the Nile River. This list focuses specifically on the natural lakes and lagoons that are inherent hydrological features of the Egyptian landscape, rather than man-made impoundments.
Lakes in Egypt
| Lake Name | Location | Surface Area (km²) | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Nasser | Aswan | 5,250 | One of the world’s largest man-made lakes, created by the Aswan High Dam. |
| Lake Manzala | Dakahlia/Port Said/Damietta | 1,360 | Egypt’s largest and most productive coastal lagoon for fisheries. |
| Toshka Lakes | New Valley | 1,300 | A series of vast, ephemeral overflow lakes from Lake Nasser in the Sahara Desert. |
| Lake Bardawil | North Sinai | 650 | A hypersaline lagoon on the Sinai Peninsula, a crucial Ramsar site for migratory birds. |
| Lake Burullus | Kafr El Sheikh | 460 | A protected wetland and the second-largest of the northern delta lagoons, rich in birdlife. |
| Great Bitter Lake | Ismailia | 250 | A natural salt lake integrated into the Suez Canal, acting as a passing lane for ships. |
| Lake Qarun | Faiyum | 230 | An ancient inland sea, now a saline lake, with nearby fossils of prehistoric whales (Wadi El Hitan). |
| Lake Mariout | Alexandria | 65 | An ancient lake near Alexandria that has separated the city from the hinterland for millennia. |
| Lake Idku | Beheira | 62 | The smallest of the four main Nile Delta coastal lagoons, supporting significant fishing activity. |
| Lower Lake (Wadi El Rayan) | Faiyum | 60 | The larger and saltier of two man-made desert lakes, featuring Egypt’s only waterfalls. |
| Siwa Salt Lakes | Siwa Oasis, Matrouh | 55 | A collection of intensely saline pools where visitors can effortlessly float, located in a remote desert oasis. |
| Upper Lake (Wadi El Rayan) | Faiyum | 50 | A freshwater reservoir in a desert depression, created to receive agricultural drainage water. |
| Little Bitter Lake | Suez | 30 | The southern extension of the Bitter Lakes system within the Suez Canal. |
| Port Fouad Lagoon | Port Said | 25 | Also known as Al-Mallaha, this shallow saline lagoon is a key area for commercial salt extraction. |
| Lake Timsah | Ismailia | 14 | Known as “Crocodile Lake,” this small lake on the Suez Canal is a center for recreation and boating. |
| Wadi El Natrun Lakes | Beheira | 10 | A chain of small alkaline lakes historically vital for producing natron salt used in ancient mummification. |
| Magic Lake | Faiyum | 0.5 | A small, picturesque lake in Wadi El Rayan known for its waters appearing to change color throughout the day. |
Images and Descriptions
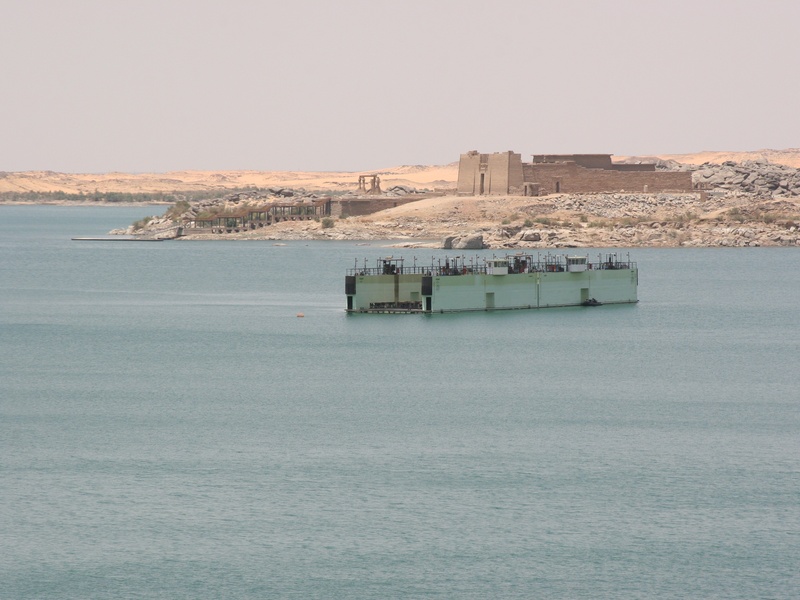

Lake Nasser
Lake Nasser is a vast artificial lake located in southern Egypt and northern Sudan. It formed after the construction of the Aswan High Dam across the Nile River. This makes it one of the largest man-made lakes globally. It provides critical water resources for irrigation and generates a significant portion of Egypt’s electricity. Its inclusion is essential for any complete list of Egyptian lakes due to its sheer size and strategic importance.
Lake Manzala
Lake Manzala is a large, brackish lagoon situated in the northeastern part of Egypt’s Nile Delta. It is the largest of the country’s northern delta lakes. This significant body of water is vital for local fishing communities and supports diverse birdlife. It connects to the Mediterranean Sea and plays a role in the region’s ecology.
Toshka Lakes
The Toshka Lakes are a series of intermittent, man-made lakes located in the Western Desert of Egypt. They formed from the overflow waters of Lake Nasser, flowing into natural depressions. These lakes are part of a massive land reclamation project aimed at creating new agricultural areas. Their size and existence can vary based on water levels from Lake Nasser.
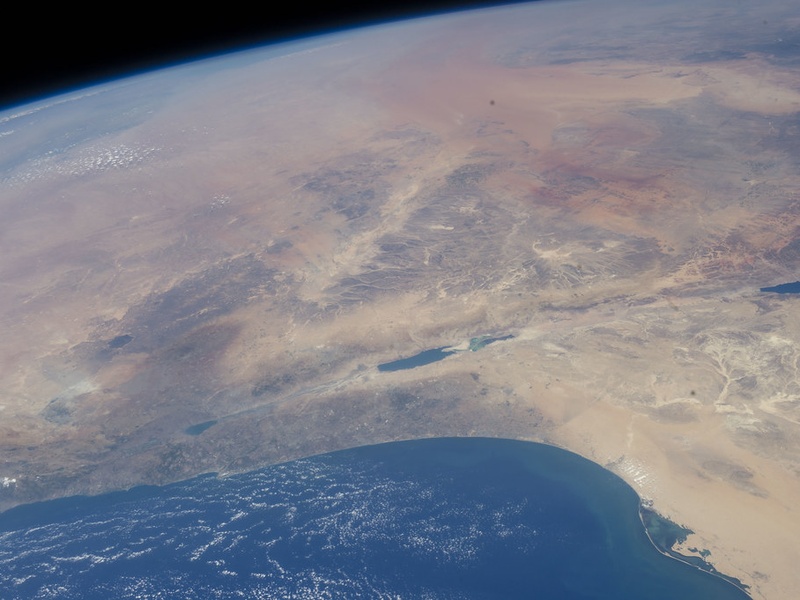

Lake Bardawil
Lake Bardawil is a large, hypersaline coastal lagoon located on the northern coast of the Sinai Peninsula. This shallow lake is one of the most saline natural bodies of water in Egypt. It is a designated protected area, known for its pristine environment and high-quality fish populations, particularly shrimp. It represents a unique ecosystem among Egypt’s lakes.
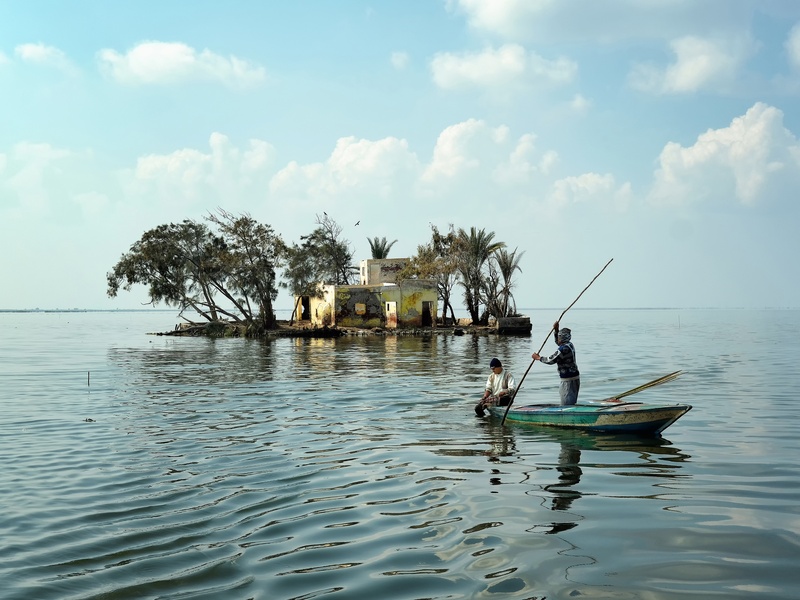

Lake Burullus
Lake Burullus is a large brackish lake situated in the northern Nile Delta region of Egypt. It ranks as the second-largest of the country’s northern delta lakes. This significant water body is crucial for local fisheries and acts as a vital wetland for migratory birds. It connects directly to the Mediterranean Sea.
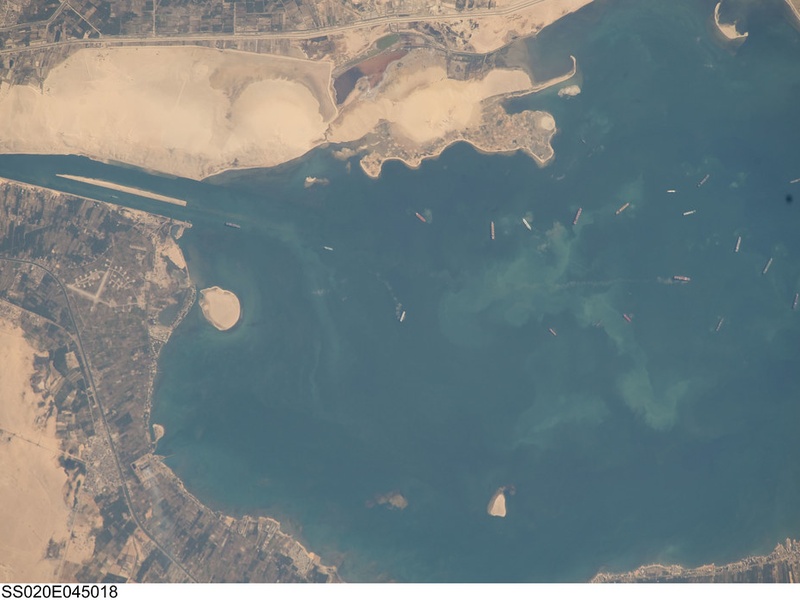

Great Bitter Lake
The Great Bitter Lake is a large saltwater lake located in Egypt, forming a key part of the Suez Canal waterway. It occupies a natural depression between the northern and southern sections of the canal. Ships passing through the Suez Canal navigate its waters. Its high salinity helps balance the water levels within the canal system.
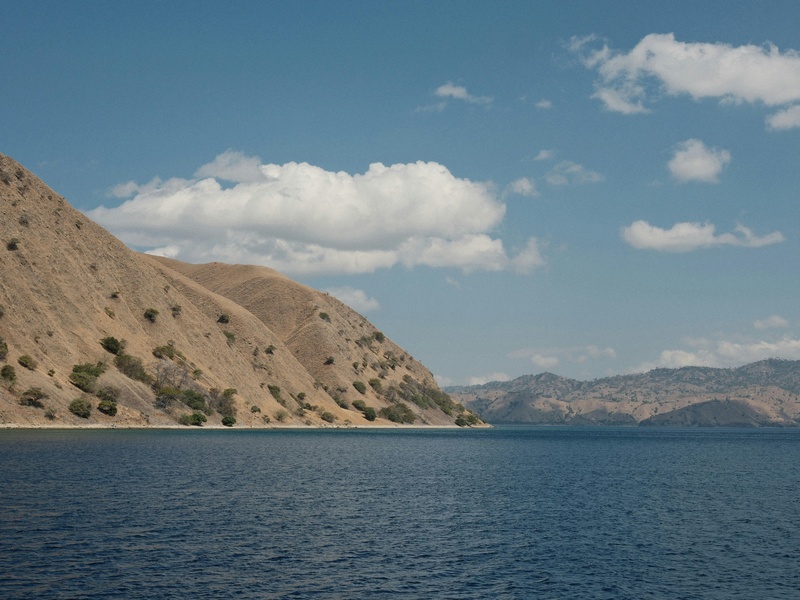

Lake Qarun
Lake Qarun is an ancient, landlocked lake located in the Fayoum Oasis of Egypt. It is one of the oldest natural lakes in the world. Originally a freshwater lake, its waters have become increasingly brackish over centuries. This lake supports local fishing industries and is a popular site for tourism and birdwatching.
Lake Mariout
Lake Mariout is a brackish lake situated near the city of Alexandria in Egypt. Historically, it was a much larger and more significant freshwater lake. Today, it serves various local industries and plays a role in the city’s drainage system. The lake faces challenges from urban development and environmental changes.
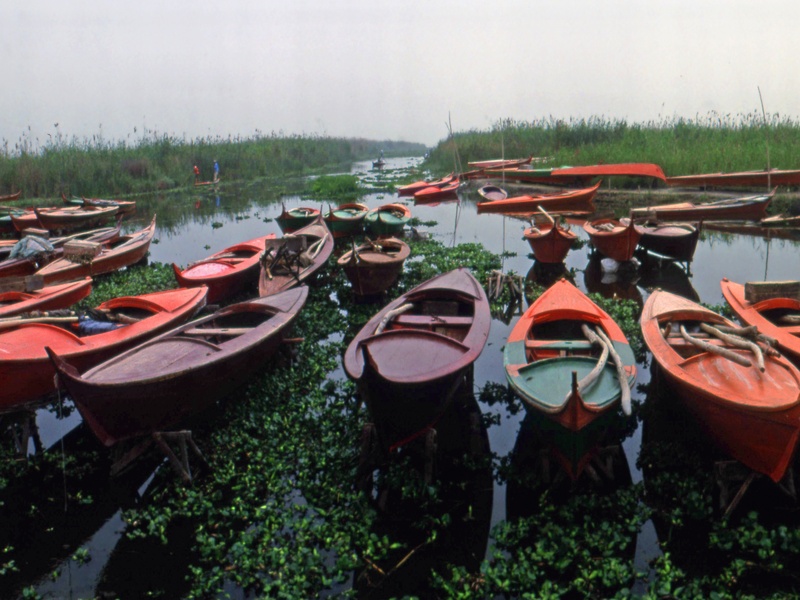

Lake Idku
Lake Idku is a brackish coastal lagoon located in the Nile Delta region of Egypt, west of the Rosetta branch. It is one of the smaller northern delta lakes. This lake supports local fishing activities and provides a habitat for various bird species. Its waters connect to the Mediterranean Sea.
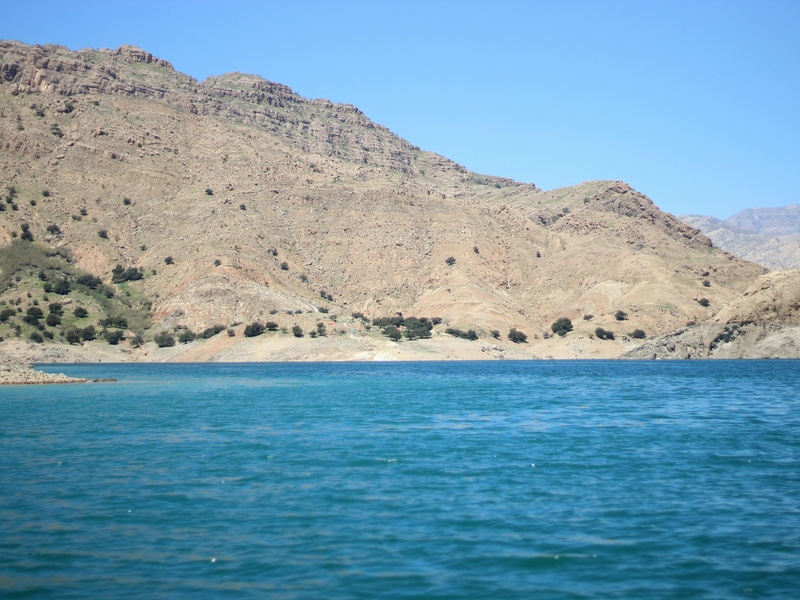

Lower Lake (Wadi El Rayan)
The Lower Lake is one of two interconnected artificial lakes in Wadi El Rayan, a protected area within the Fayoum Oasis. This lake was created to manage drainage water from the Fayoum agricultural lands. It is a vital part of the Wadi El Rayan Protected Area, supporting diverse wildlife and aquatic life.
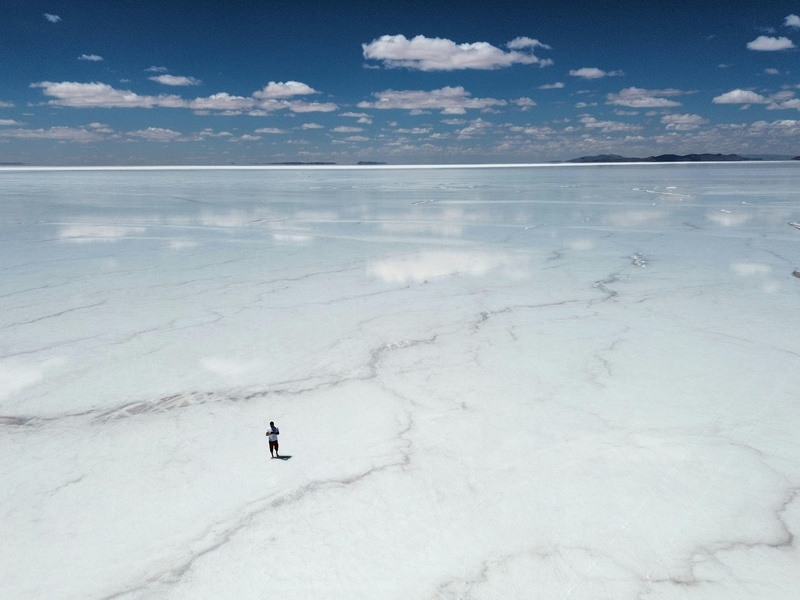

Siwa Salt Lakes
The Siwa Salt Lakes are a collection of highly saline lakes found in the remote Siwa Oasis in Egypt’s Western Desert. These natural lakes are known for their extremely high salt content, which creates unique blue-green waters. They are a source of salt for local communities and a growing attraction for tourists seeking therapeutic bathing. They are key inclusions for demonstrating Egypt’s diverse aquatic environments.
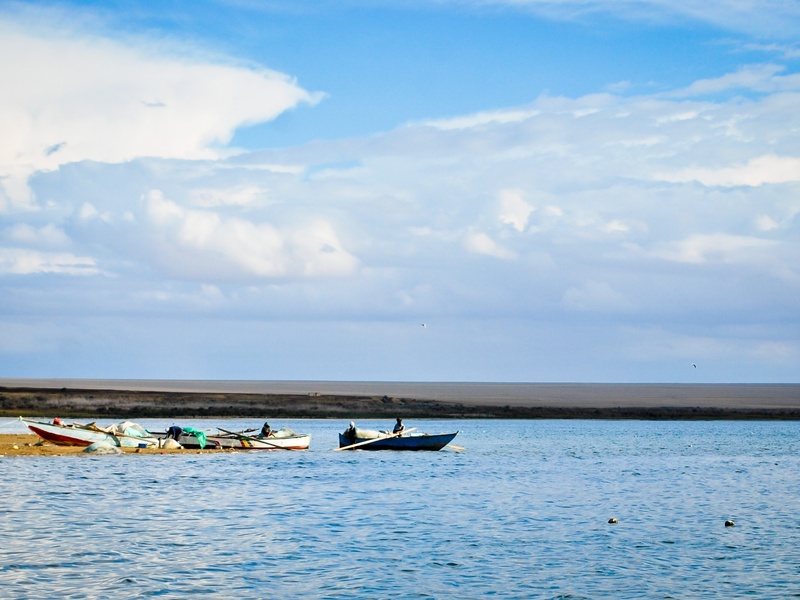

Upper Lake (Wadi El Rayan)
The Upper Lake is one of two artificial lakes located within the Wadi El Rayan Protected Area in the Fayoum Oasis. This lake receives drainage water from agricultural areas and connects to the Lower Lake. It helps manage water levels in the region and provides an important habitat for aquatic species and birds.
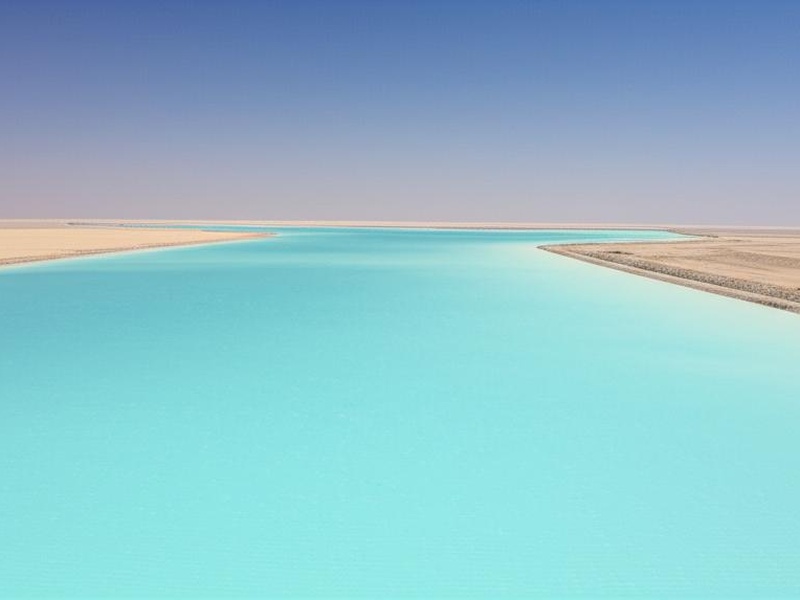

Little Bitter Lake
The Little Bitter Lake is a saltwater lake forming another segment of the Suez Canal in Egypt. It lies to the south of the Great Bitter Lake and connects the canal’s central and southern sections. This natural depression allows ships to pass through the waterway. Its waters are saline, similar to its larger counterpart.
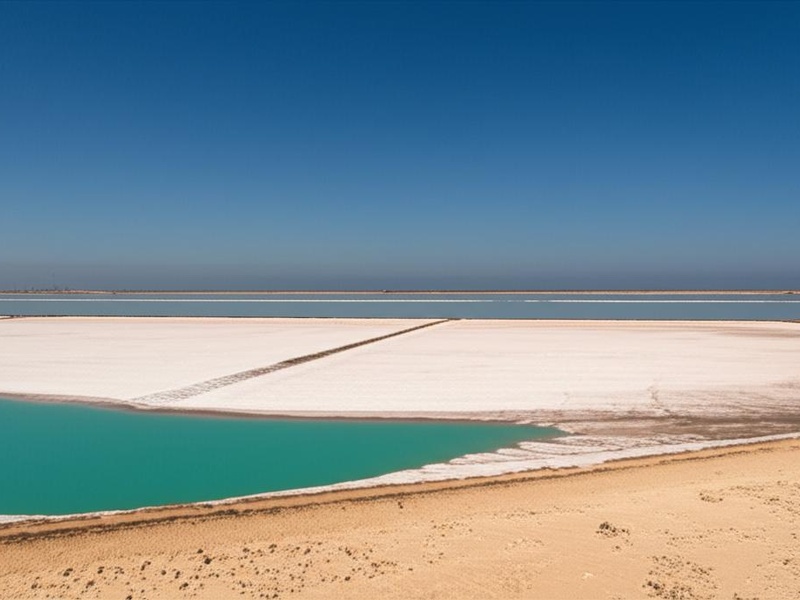

Port Fouad Lagoon
Port Fouad Lagoon is a coastal body of water located near the city of Port Fouad in Egypt. It is connected to the Mediterranean Sea and often considered part of the larger Lake Manzala ecosystem. This lagoon supports local fishing activities and contributes to the biodiversity of Egypt’s northern coast.

Lake Timsah
Lake Timsah is a saltwater lake in Egypt that forms part of the Suez Canal waterway. It is a natural depression located near the city of Ismailia. The lake serves as a significant recreational area for locals and a stopping point for ships transiting the canal. Its waters contribute to the canal’s overall system.
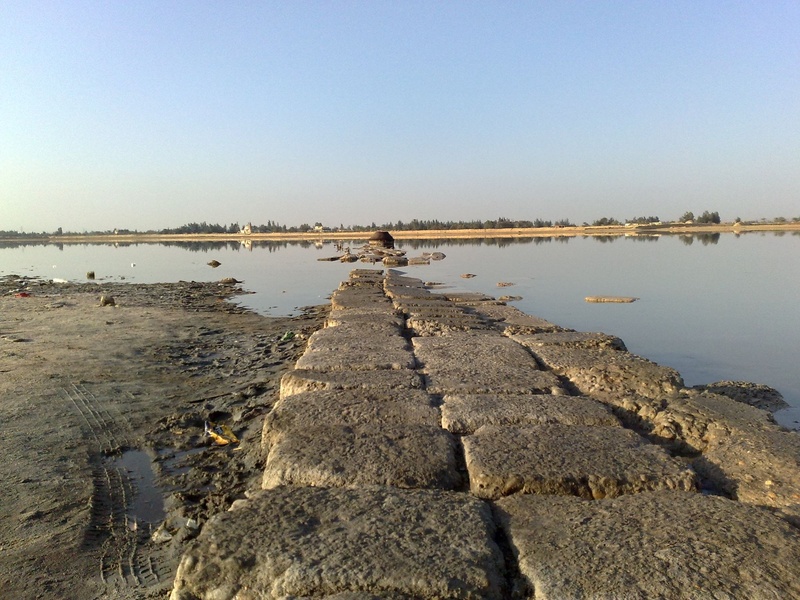

Wadi El Natrun Lakes
The Wadi El Natrun Lakes are a series of highly alkaline, saline lakes located in a desert valley in Egypt. These lakes are historically significant, surrounded by ancient Coptic monasteries. They are known for their unique chemical composition and were historically a source of natron, a natural mineral salt used in mummification.

Magic Lake
Magic Lake is a natural lake located in the Fayoum Oasis of Egypt, often found within or near the Wadi El Rayan Protected Area. It is known for its remarkable ability to change colors throughout the day, depending on sunlight and mineral content. This unique feature makes it a popular tourist destination.