Poland has experienced remarkable economic growth and transformation over the past few decades, evolving into a dynamic European economy. Its cities, from the historic centers to burgeoning industrial hubs, each contribute uniquely to the nation’s prosperity, attracting investment, fostering innovation, and providing diverse opportunities for residents and businesses alike.
If you’re curious about the urban centers leading this economic charge, this detailed list reveals the Richest Cities in Poland. We’ve meticulously compiled data for 15 cities, showcasing an impressive economic spectrum ranging from the strong industrial base of Bielsko-Biała to the vibrant, diverse economy of Wrocław. For each entry, you’ll find key information including its Country, GDP per capita (PLN), and Key Industries, providing a comprehensive overview of their financial standing and economic drivers below.
How is a city’s wealth typically measured in Poland?
A city’s economic strength is most commonly assessed using metrics like GDP per capita, which reflects the average economic output per person within its administrative boundaries. Other important indicators include average disposable income, the concentration of high-value industries, robust local business activity, and the level of foreign and domestic investment, all contributing to an understanding of its overall prosperity.
Do these wealthy cities also have the largest populations in Poland?
Not always. While some of Poland’s wealthiest cities are indeed major population centers, like Wrocław, economic prosperity isn’t strictly proportional to population size. Cities with a smaller population can achieve high GDP per capita if they possess highly specialized, high-value industries, strong export-oriented sectors, or a significant presence of innovative companies that generate substantial economic output per resident.
Richest Cities in Poland
| City | Country | GDP per capita (PLN) | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Płock | Poland | 350,000 | Oil refining, petrochemicals, energy |
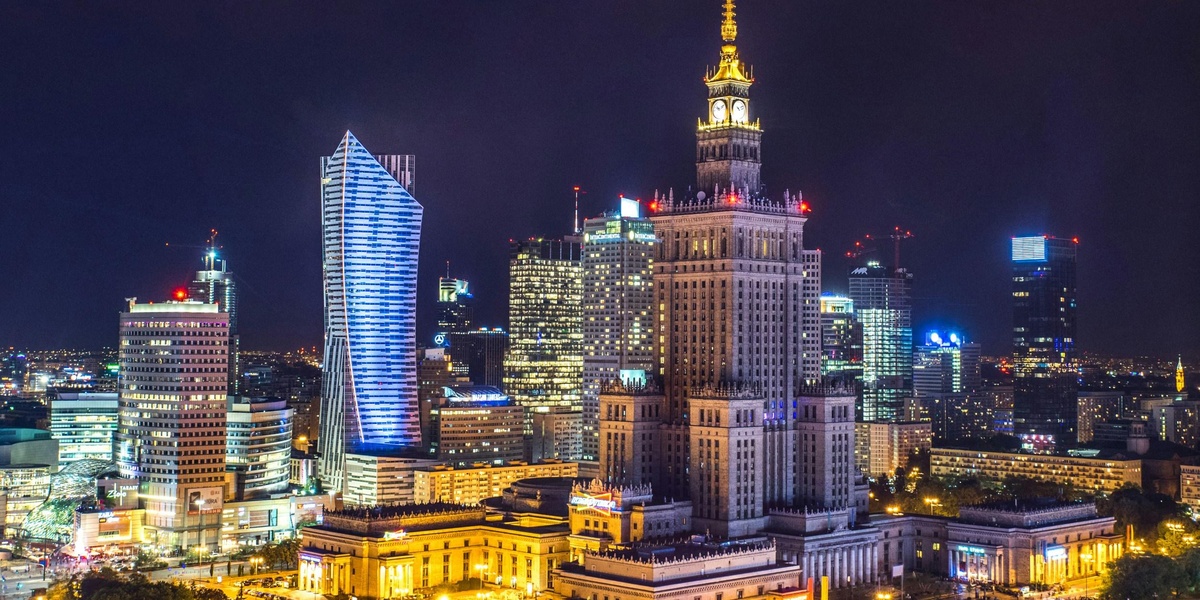
| Warsaw | Poland | 200,000 | Finance, services, tech, government |
| Kędzierzyn-Koźle | Poland | 300,000 | Chemicals, petrochemicals, heavy industry |
| Tychy | Poland | 220,000 | Automotive manufacturing, industry, engineering |
| Gliwice | Poland | 170,000 | Automotive, machinery, R&D, advanced manufacturing |
| Poznań | Poland | 150,000 | Trade, manufacturing, services, logistics |
| Katowice | Poland | 150,000 | Business services, coal conversion, industry, commerce |
| Wrocław | Poland | 145,000 | IT, BPO, manufacturing, academia |
| Kraków | Poland | 140,000 | IT, tourism, finance, education |
| Gdańsk | Poland | 140,000 | Shipbuilding, ports, logistics, petrochemicals |
| Gdynia | Poland | 135,000 | Ports, shipping, maritime services, industry |
| Sopot | Poland | 180,000 | Tourism, hospitality, real estate, services |
| Bielsko-Biała | Poland | 130,000 | Automotive suppliers, textiles, precision engineering |
| Rzeszów | Poland | 125,000 | Aviation, IT, R&D, manufacturing |
| Szczecin | Poland | 115,000 | Ports, shipbuilding, logistics, industry |
Images and Descriptions
Płock
Płock is a petrochemical powerhouse anchored by the PKN Orlen refinery; its large industrial output per resident drives one of Poland’s highest GDP per capita figures, making it economically outsized for its population.

Warsaw
Poland’s capital and economic hub, Warsaw concentrates finance, corporate HQs, government institutions and a booming tech sector, producing high wages and substantial economic output per person.
Kędzierzyn-Koźle
Kędzierzyn-Koźle hosts major chemical complexes whose high-value industrial output lifts GDP per capita, making this relatively small city one of Poland’s richest by productivity.

Tychy
Tychy combines large-scale automotive manufacturing and industrial plants with a modest population, producing very high economic output per resident and strong average incomes.

Gliwice
Gliwice is an industrial and technology centre in Upper Silesia with strong automotive and advanced manufacturing clusters, driving high productivity and skilled employment.

Poznań
Poznań is a major trade and logistics hub with diverse manufacturing and services sectors, historically strong business environment and high average incomes.

Katowice
Katowice anchors Upper Silesia’s economy, shifting from heavy industry to services and corporate centers, with significant business services and industrial output per capita.

Wrocław
Wrocław mixes a vibrant IT and services sector with manufacturing and universities, attracting skilled workers and multinational investment that boost local prosperity.

Kraków
Kraków blends tourism and cultural assets with a strong IT and services sector and large universities, producing high incomes and sustained economic growth.

Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a Baltic economic hub with ports, logistics, shipbuilding and nearby petrochemical activity, generating substantial output and trade-linked prosperity.

Gdynia
Gdynia complements Gdańsk as part of the Tricity agglomeration, with maritime services, shipping and industry contributing to high per-capita economic performance.

Sopot
Sopot is a small but affluent seaside resort known for high-value tourism, upscale real estate and services, resulting in elevated average incomes and wealth indicators.

Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała hosts advanced manufacturing and automotive supply chains, combining industrial tradition with modern engineering firms that support strong local wages.

Rzeszów
Rzeszów has developed rapidly around aviation, aerospace suppliers, IT and R&D, becoming a dynamic regional center with rising incomes and investment.

Szczecin
Szczecin is a key Baltic port and industrial center; its shipping, logistics and manufacturing sectors sustain notable economic output and regional importance.






