Greece wears its history on every hillside and shoreline, from ancient citadels to Bronze Age ports. Whether you’re planning a focused history trip or browsing for inspiration, a clear list makes it easier to spot patterns, eras, and why each place matters.
There are 68 Historical Places in Greece, ranging from Acrocorinth to Zakros. For each site you’ll find below entries organized as Location, Era (period), Significance, so you can quickly compare dates, themes, and why a stop is worth your time — you’ll find below.
How can I use this list to plan an efficient visit to multiple sites?
Group sites by Era (period) and geographic proximity: visiting nearby Classical or Byzantine sites in one day saves travel time, while noting Significance helps prioritize those that match your interests (architecture, warfare, religion).
Are these places generally open to visitors and how do I check access or restrictions?
Many are public sites or museums with seasonal hours and occasional closures for conservation; check official site or local archaeological service pages before traveling, and look for visitor information in the Significance field below for access notes.
Historical Places in Greece
| Name | Location | Era (period) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acropolis of Athens | Athens | Classical 5th c. BCE | Iconic citadel dominated by the Parthenon; symbol of ancient Greece |
| Parthenon | Athens | Classical 5th c. BCE | Masterpiece Doric temple dedicated to Athena on the Acropolis |
| Ancient Agora | Athens | Classical–Hellenistic | Marketplace and civic center with Stoa of Attalos and archaeological museum |
| Temple of Hephaestus | Athens (Agora) | Classical 5th c. BCE | Best-preserved Greek temple overlooking the Ancient Agora |
| Theatre of Dionysus | Athens | Classical | Earliest Greek theatre; birthplace of ancient drama |
| Kerameikos | Athens | Archaic–Classical | Ancient cemetery and archaeological site with funerary monuments |
| Temple of Olympian Zeus | Athens | Classical–Roman | Massive temple completed in Roman era; colossal Corinthian columns |
| Sounion (Temple of Poseidon) | Cape Sounion, Attica | Classical 5th c. BCE | Dramatic clifftop temple with sunset sea views |
| Delphi | Delphi, Phocis | Archaic–Classical | Pan-Hellenic sanctuary of Apollo; famous oracle and stadium |
| Sanctuary of Athena Pronaia | Delphi | Archaic–Classical | Distinctive tholos and sanctuary complex near Delphi |
| Olympia | Olympia, Elis | Archaic–Classical | Site of ancient Olympic Games; archaeological site and stadium |
| Temple of Zeus (Olympia) | Olympia | Classical | Once housed monumental statue of Zeus by Phidias |
| Stadium of Olympia | Olympia | Archaic–Classical | Archaeological stadium where ancient Olympic competitions occurred |
| Mycenae | Mycenae, Argolis | Late Bronze Age (c.1600–1100 BCE) | Palatial ruins, Lion Gate and royal tombs of Homeric age |
| Tiryns | Tiryns, Argolis | Late Bronze Age | Cyclopean fortress with massive stone walls; Mycenaean stronghold |
| Epidaurus | Argolida | Classical | Famed ancient theater renowned for acoustics; healing sanctuary of Asclepius |
| Ancient Corinth | Corinth | Archaic–Classical | Major city-state ruins; Temple of Apollo and Roman forum |
| Acrocorinth | Corinth | Byzantine–Medieval | Imposing acropolis fortress with multi-period fortifications and panoramic views |
| Nemea | Nemea, Corinthia | Archaic–Classical | Pan-Hellenic sanctuary and stadium associated with athletic games |
| Mystras | Sparta, Laconia | Byzantine (13th–15th c.) | Well-preserved Byzantine fortified town; palaces, churches and monasteries |
| Monemvasia | Monemvasia, Laconia | Medieval | Byzantine and Venetian fortress town built on a sea rock |
| Palamidi Fortress | Nafplio, Argolis | Venetian 18th c. | Well-preserved Venetian fortress dominating Nafplio harbor |
| Bourtzi | Nafplio | Medieval–Venetian | Small island fortress guarding Nafplio harbor |
| Ancient Messene | Kalamata region, Messenia | Hellenistic | Extensive planned city ruins with theater and fortifications |
| Palace of Nestor | Pylos, Messenia | Mycenaean | Large Mycenaean palace with Linear B tablets and frescoes |
| Vergina (Aigai) | Vergina, Imathia | Late Bronze–Classical | Royal tombs of Macedon, including Philip II’s tomb (rich finds) |
| Pella | Pella, Central Macedonia | Classical | Capital of ancient Macedonia; royal palace and mosaics |
| Philippi | Kavala regional unit | Hellenistic–Roman | Important Roman/Christian city with forum, basilicas and theater |
| Amphipolis | Amphipolis, Serres | Classical–Hellenistic | Site of lion monument and monumental tombs from Macedonian era |
| Dion | Litochoro, Pieria | Hellenistic–Roman | Sanctuary at Mount Olympus with temples, theaters and mosaics |
| Mount Athos | Chalkidiki | Byzantine onward | Monastic community with medieval monasteries and Byzantine art |
| Meteora | Kalambaka, Thessaly | Byzantine onward | Spectacular cliff-top monasteries built on sandstone pillars |
| Thessaloniki Rotunda | Thessaloniki | Roman–Byzantine | Massive Roman rotunda converted into church and mosque; historic monument |
| White Tower | Thessaloniki | Ottoman 15th c. | Iconic Ottoman-era tower and city symbol |
| Byzantine Walls of Thessaloniki | Thessaloniki | Byzantine | Impressive medieval fortifications encircling old city |
| Dodona | Ioannina, Epirus | Archaic–Classical | Ancient oracle sanctuary with large open-air theatre |
| Akrotiri (Thera) | Santorini | Late Bronze Age (Minoan) | Prehistoric Minoan town preserved by volcanic ash |
| Delos | Delos Island, Cyclades | Archaic–Hellenistic | Sacred island with extensive ruins linked to Apollo cult |
| Knossos | Heraklion, Crete | Minoan (c.2000–1,450 BCE) | Largest Bronze Age Minoan palace complex; myth of the Minotaur |
| Phaistos | Phaistos, Crete | Minoan | Minoan palace ruins and clay disk discovery site |
| Malia | Malia, Crete | Minoan | Minoan palace complex with courtyard and archaeological remains |
| Zakros | Zakros, Crete | Late Minoan | Remote palace site with Linear A finds and coastal views |
| Gortyna | Gortyna, Crete | Hellenistic–Roman | Roman-era law code inscriptions and ancient city ruins |
| Roman Agora of Athens | Athens | Roman | Roman marketplace featuring preserved monuments including Tower of the Winds |
| Temple of Apollo at Bassae | Andritsaina, Arcadia | Classical 5th c. BCE | Well-preserved unique temple with Ionic, Doric and Corinthian features |
| Ancient Thera | Santorini (Mesa Vouno) | Hellenistic–Roman | Hilltop city ruins spanning Hellenistic to Byzantine periods |
| Kamiros | Rhodes | Archaic–Hellenistic | One of three ancient cities of Rhodes with grid plan remains |
| Lindos Acropolis | Lindos, Rhodes | Archaic–Classical | Acropolis with Hellenistic, Roman and medieval remains overlooking the sea |
| Rhodes Old Town | Rhodes | Medieval (Knights Hospitaller) | Extensive medieval walled city and the Palace of the Grand Master |
| Palace of the Grand Master | Rhodes Old Town | Medieval | Fortified palace of the Knights of Rhodes; museum and landmark |
| Ancient Sparta | Sparta, Laconia | Archaic–Classical | Ruins of Sparta’s public buildings and Roman baths near Byzantine city |
| Ancient Theater of Mytilene | Mytilene, Lesbos | Hellenistic–Roman | Large ancient theater overlooking the sea |
| Ancient Eretria | Eretria, Euboea | Archaic–Classical | Complex with temples, theater and house ruins |
| Thermopylae battlefield | Thermopylae, Phthiotis | Classical 480 BCE | Famous battle site where Leonidas fought Persians; monument present |
| Plataea | Plataea, Boeotia | Classical | Site of decisive 479 BCE Greek victory over Persians; memorial remains |
| Marathon | Marathon, Attica | Classical 490 BCE | Battlefield of Marathon with burial tumulus and monument |
| Temple of Aphaia | Aegina, Saronic Gulf | Archaic 5th c. BCE | Well-preserved Doric temple on Aegina hilltop |
| Spinalonga | Spinalonga (Elounda), Crete | Venetian–Modern | Fortified island; Venetian fortress and later leper colony |
| Chlemoutsi Castle | Kyllini, Elis | Frankish 13th c. | Medieval castle built by Crusader princes in Peloponnese |
| Arkadi Monastery | Rethymno, Crete | Ottoman 16th c. | Monastery known for 1866 Cretan revolt and sacrifice of locals |
| Corfu Old Fortress | Corfu Town, Corfu | Venetian–Ottoman | Venetian-built fortress overlooking Corfu harbour |
| Treasury of Atreus | Mycenae | Late Bronze Age | Stunning beehive (tholos) tomb with monumental facade |
| Franchthi Cave | Kastraki, Argolis | Palaeolithic–Neolithic | Important prehistoric cave with continuous human occupation evidence |
| Petralona Cave | Petralona, Chalkidiki | Pleistocene | Prehistoric cave with early hominid skull and Paleolithic finds |
| Nicopolis | Preveza/Gulf of Ambracia | Roman (Augustan) | City founded by Augustus after Actium; Roman ruins and museum |
| Olynthos | Olynthos, Chalkidiki | Classical | Planned Classical city with well-preserved houses and mosaics |
| Rhamnous | Rhamnous, Attica | Classical | Sanctuary of Nemesis with strategic coastal position and ruins |
| Helike | Aigion region, Achaea | Archaic (submerged 373 BCE) | Ancient city submerged after earthquake; archaeological remains underwater |
Images and Descriptions
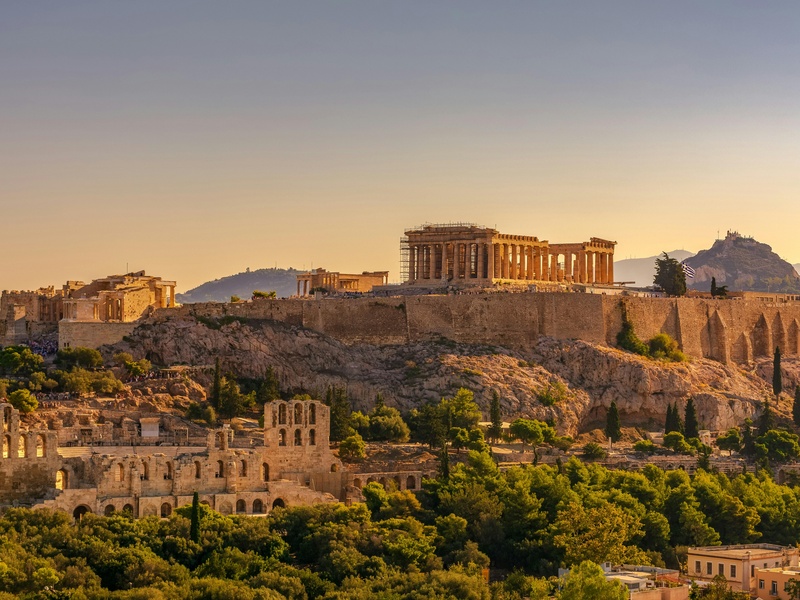

Acropolis of Athens
Prominent ancient citadel on a limestone hill above Athens. Date: mainly Classical era (5th century BCE). Serve as the religious and ceremonial center of ancient Athens. Contain several major monuments that define Classical Greek architecture and civic pride. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status as part of the Acropolis group.
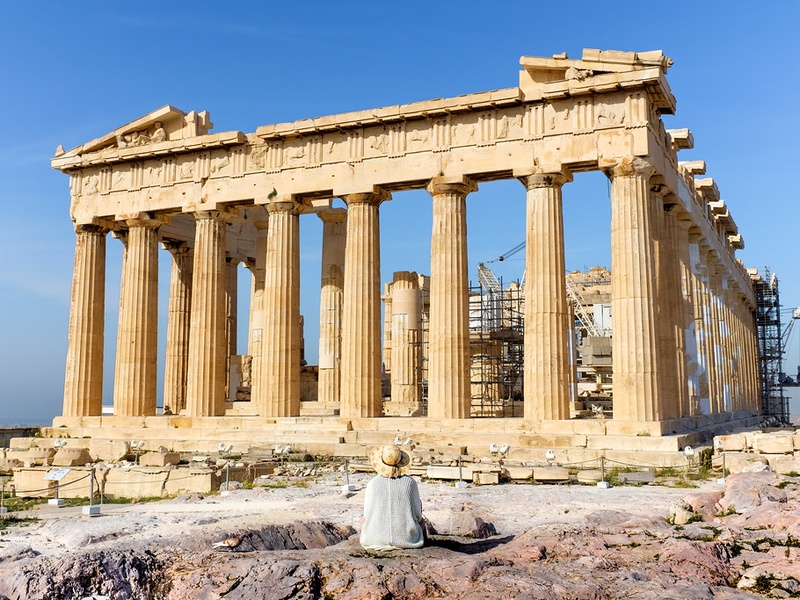

Parthenon
Iconic Doric temple on the Acropolis built in the 5th century BCE. Dedicate to the goddess Athena. Represent the height of Classical Greek art and architecture. Show sculptural decoration that influenced Western art for centuries.

Ancient Agora
Market and civic center north of the Acropolis in Athens. Flourish from the Archaic through the Roman period. Act as the social, political, and commercial heart of the city. Preserve ruins, stoas, and the reconstructed Stoa of Attalos museum.
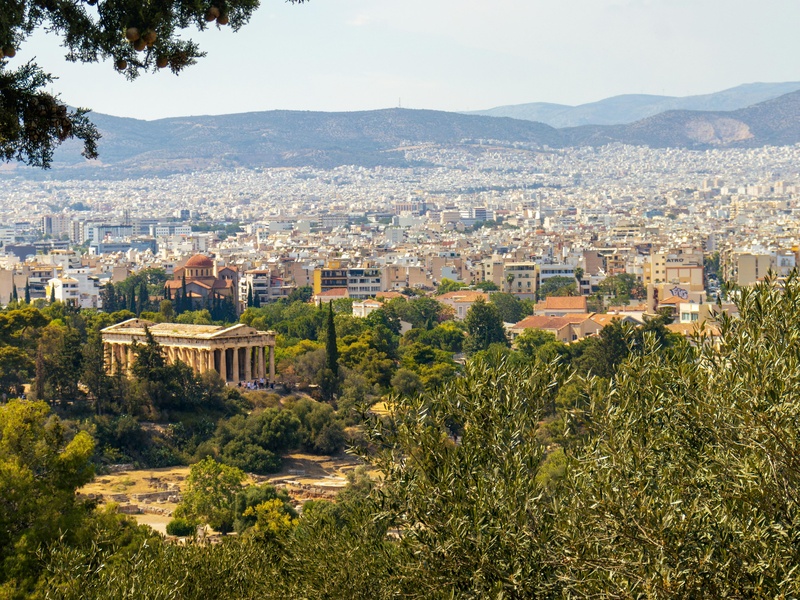

Temple of Hephaestus
Well-preserved Doric temple in the Ancient Agora of Athens. Date: late 5th century BCE. Dedicate to Hephaestus and Athena Ergane. Serve as a rare example of a nearly intact classical temple and offer insight into everyday worship.
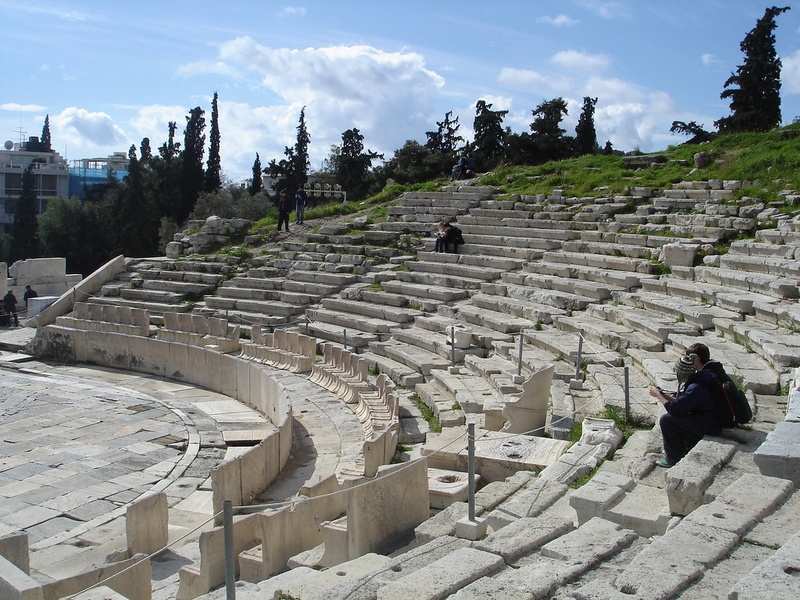

Theatre of Dionysus
Large open-air theatre on the south slope of the Acropolis. Date: origins in the 5th century BCE. Host ancient dramatic performances and festival competitions. Influence modern theatre with its architectural and acoustic design.
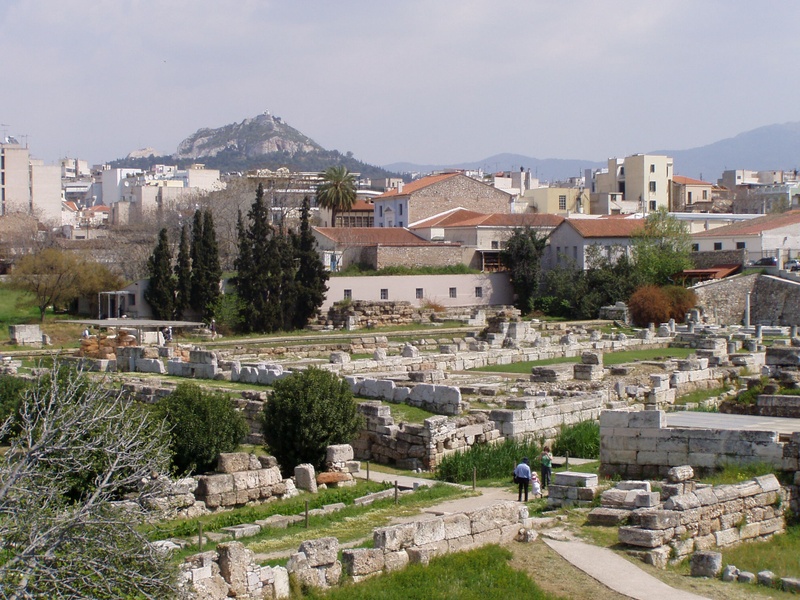

Kerameikos
Ancient cemetery and potters quarter northwest of the Acropolis. Date: Archaic through Roman periods. Serve as the main burial ground of ancient Athens and show funerary monuments and city walls. Provide evidence of daily life and death rites.

Temple of Olympian Zeus
Massive temple in central Athens begun in the 6th century BCE and completed under Roman rule. Honor Zeus with grand Corinthian columns. Represent imperial patronage and Hellenistic-Roman architectural fusion. Stand as one of Greece’s largest ancient temples.

Sounion (Temple of Poseidon)
Clifftop temple at Cape Sounion overlooking the Aegean Sea. Date: 5th century BCE. Dedicate to Poseidon and mark a key maritime landmark for ancient sailors. Offer dramatic sea views and well-preserved classical columns.
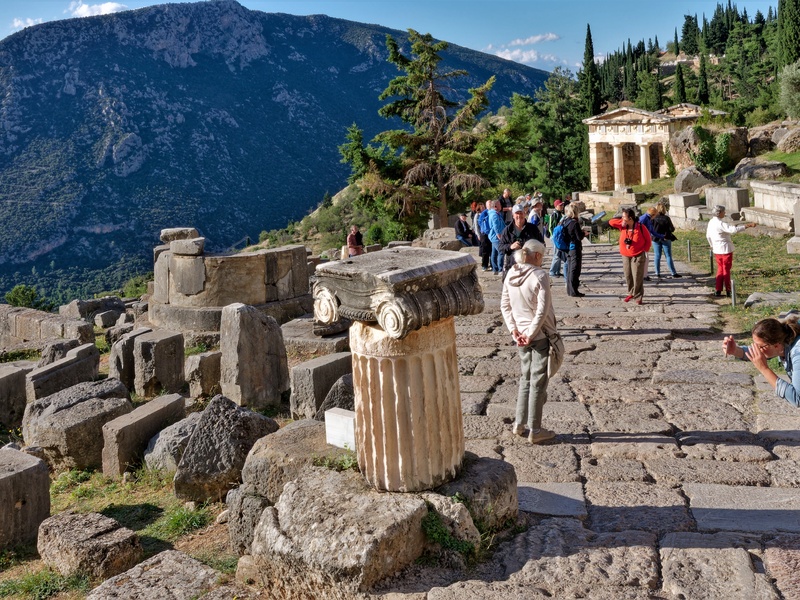

Delphi
Panhellenic sanctuary on Mount Parnassus. Date: Archaic to Roman periods. Host the Oracle of Apollo, the center of Greek religious consultation and pan-Hellenic festivals. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status for its cultural and historic importance.
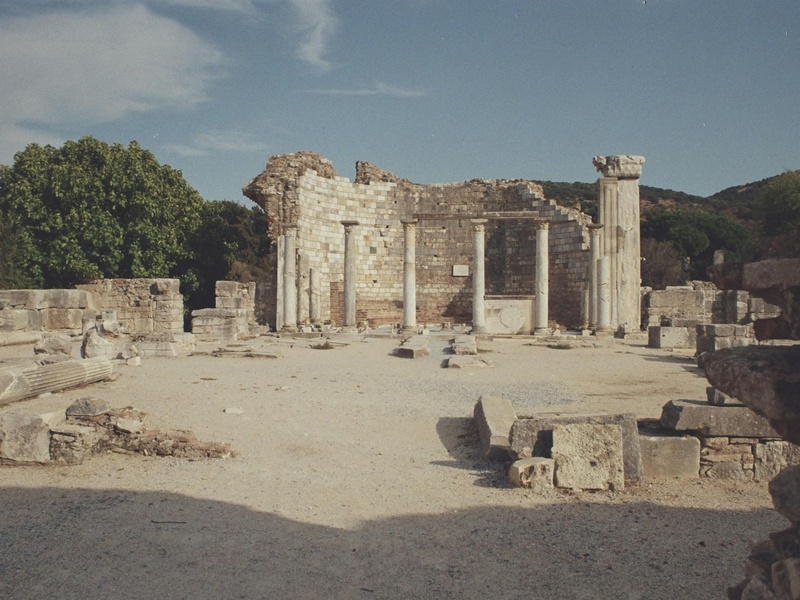

Sanctuary of Athena Pronaia
Religious site at Delphi near the main sanctuary. Date: Archaic through Classical periods. Contain the Tholos, a circular building of striking design, and other temples. Serve as part of the larger Delphi sacred landscape.

Olympia
Ancient sanctuary in the Peloponnese and birthplace of the Olympic Games. Date: Archaic through Roman periods. Host athletic competitions, religious rites, and monumental architecture like the Temple of Zeus. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status as a symbol of ancient sport.

Temple of Zeus (Olympia)
Grand temple at Olympia built in the 5th century BCE. House a large chryselephantine statue of Zeus in antiquity. Serve as a key religious and artistic center in the sanctuary complex. Influence Hellenistic and Roman temple design.
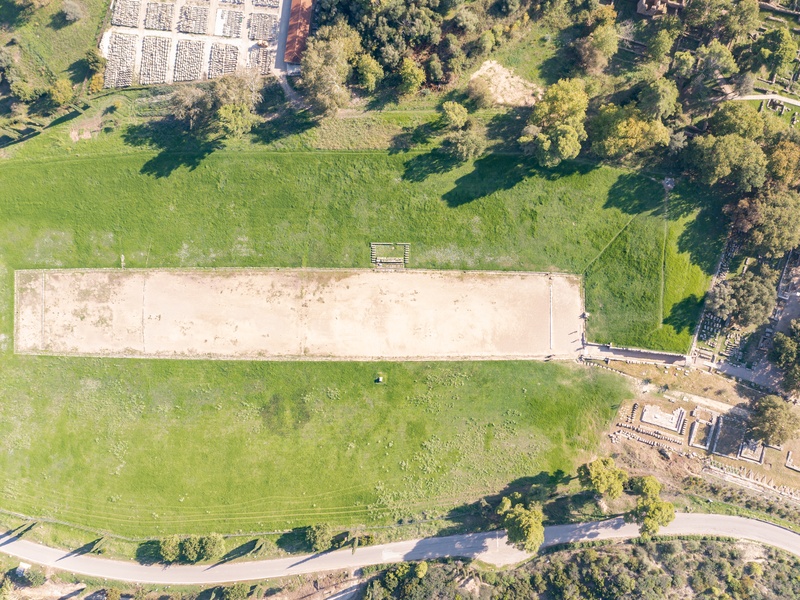

Stadium of Olympia
Ancient athletic stadium at Olympia. Date: developed from the 8th century BCE onward. Host the ancient Olympic Games and foot races held in honor of Zeus. Preserve starting boxes and a clear stadium layout for study and visits.
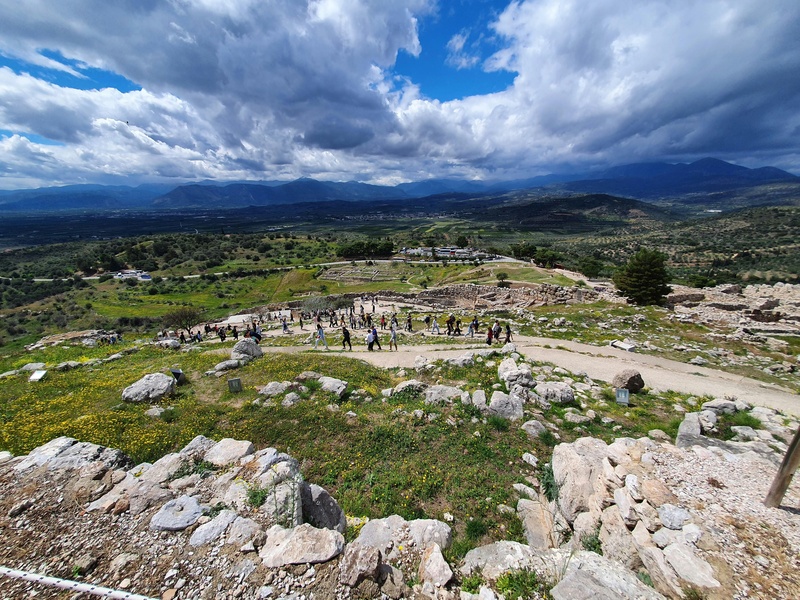

Mycenae
Fortified Bronze Age citadel in the Peloponnese. Date: Late Bronze Age (c.1600–1100 BCE). Serve as the center of Mycenaean civilization and feature the Lion Gate, royal tombs, and palatial ruins. Influence understanding of Homeric Greece.

Tiryns
Cyclopean-walled Bronze Age fortress near Mycenae. Date: Late Bronze Age. Feature massive stone walls and palace complexes. Show defensive architecture and royal power in Mycenaean Greece.
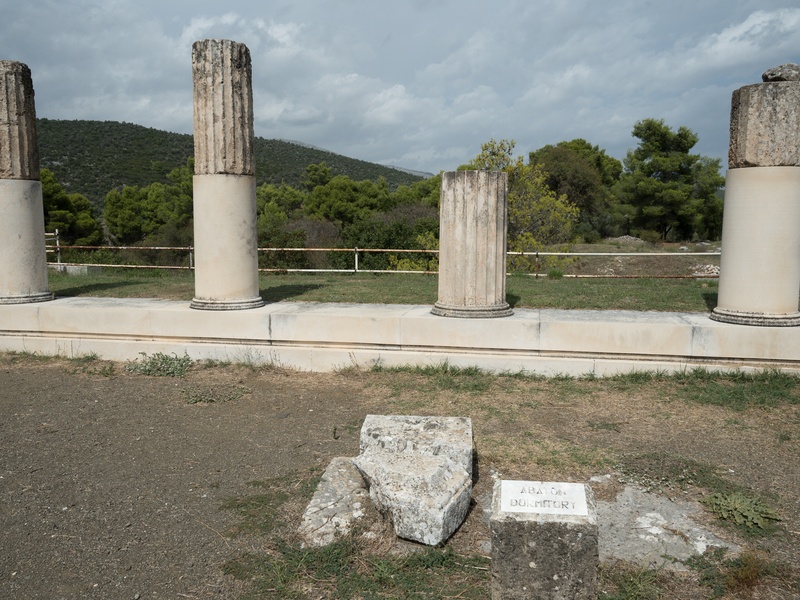

Epidaurus
Ancient sanctuary dedicated to the healing god Asclepius. Date: Classical period. Contain one of the best-preserved ancient theatres with exceptional acoustics. Serve as a major health and religious center and remain a living performance venue.

Ancient Corinth
Important city-state at the Isthmus of Corinth. Date: Archaic through Roman periods. Control trade routes and exhibit urban planning, markets, and the Temple of Apollo. Reflect strategic and economic power in ancient Greece.

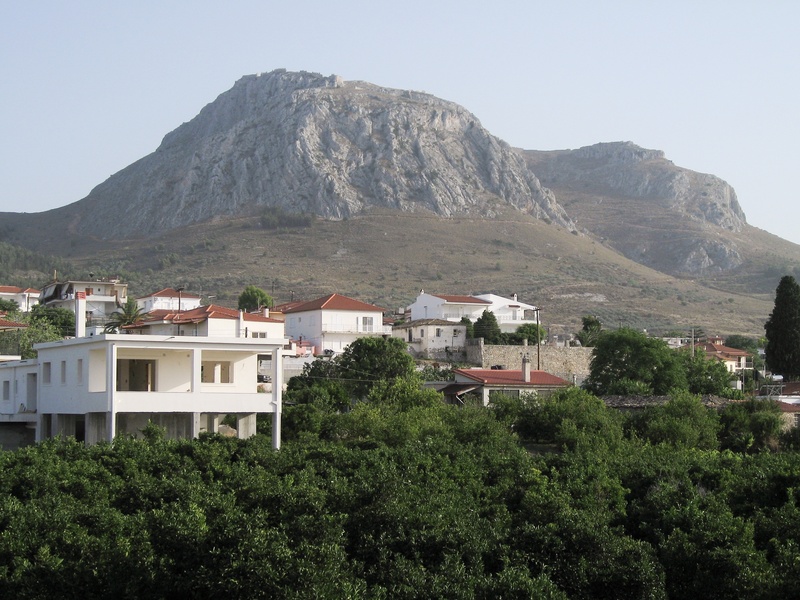
Acrocorinth
Steep fortified acropolis above ancient Corinth. Date: Classical to Ottoman periods. Serve as a long-used stronghold with layered fortifications. Offer strategic views and a record of continuous occupation.
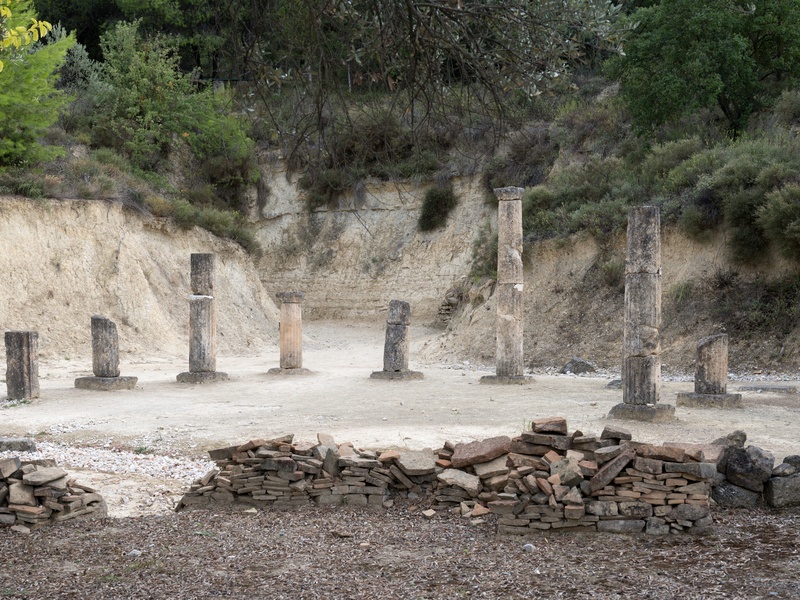

Nemea
Panhellenic sanctuary in the northeastern Peloponnese. Date: Archaic and Classical periods. Host the Nemean Games and honor Zeus. Contain a well-preserved stadium, temple remains, and archaeological museum.
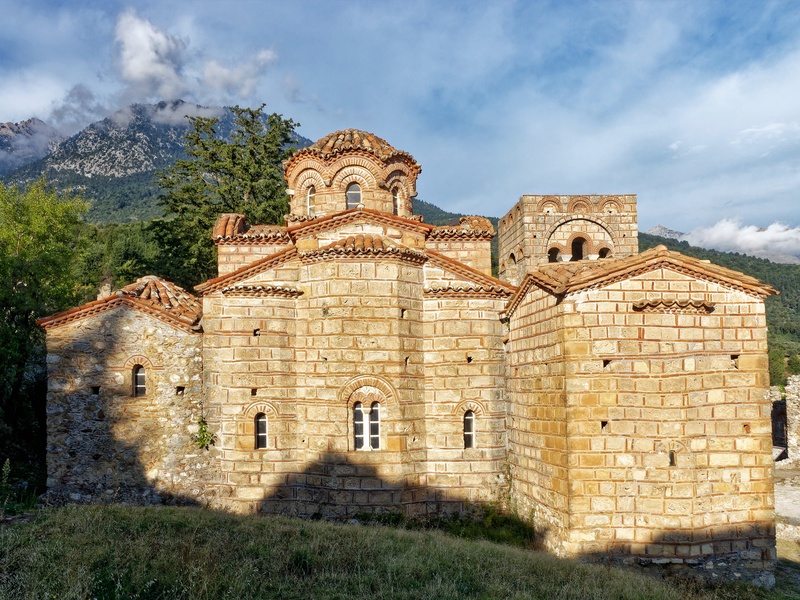

Mystras
Byzantine fortified town near Sparta. Date: 13th–15th centuries. Serve as a major Late Byzantine cultural and religious center. Preserve churches, palaces, and monasteries in a dramatic hillside site; include UNESCO recognition as part of Mystras site listings.
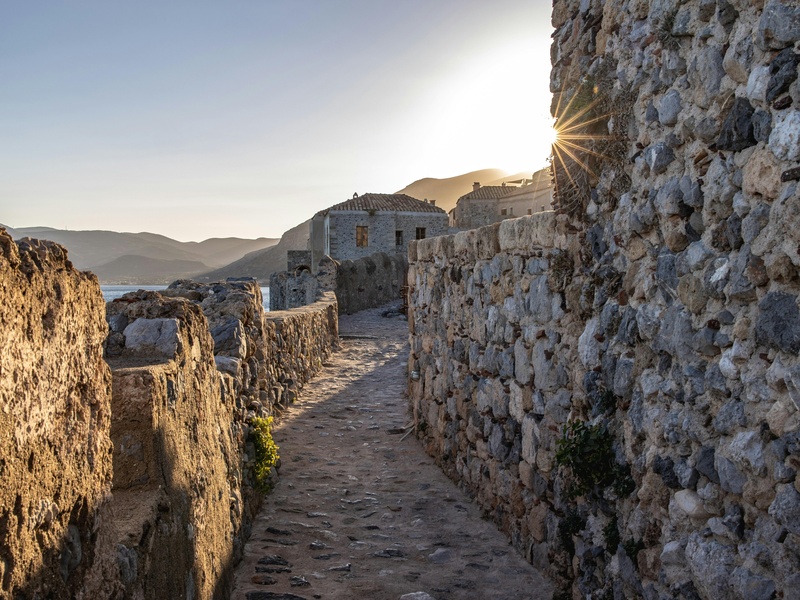

Monemvasia
Medieval fortress town on a small island off the Peloponnese. Date: Byzantine through Venetian periods. Contain narrow lanes, Byzantine churches, and preserved fortifications. Represent medieval trade and defensive island settlements.
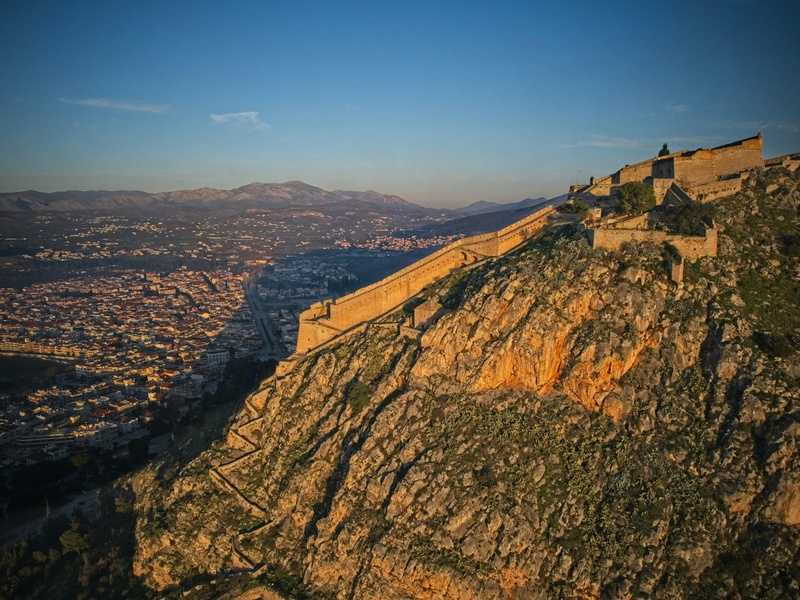

Palamidi Fortress
Venetian-built fortress overlooking Nafplio. Date: early 18th century. Command the bay with extensive fortifications and bastions. Showcase Venetian military architecture and panoramic views.
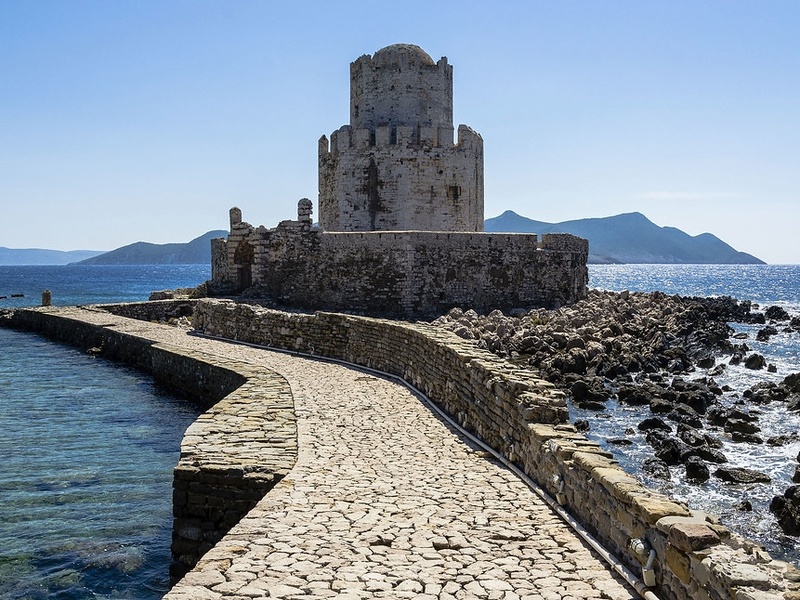

Bourtzi
Small islet fortress in the harbor of Nafplio. Date: Venetian period, 15th–16th centuries. Serve as a defensive outpost and later as a salt depot and prison. Present a compact example of coastal fortification.
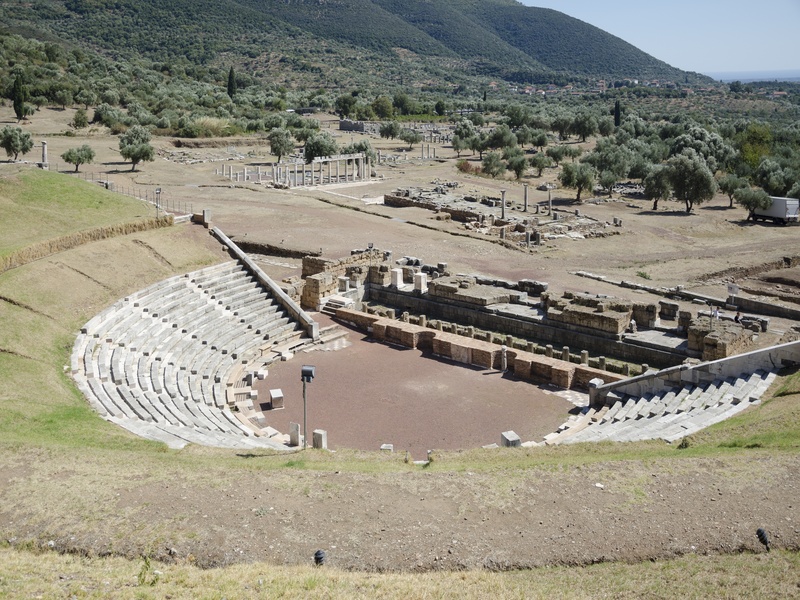

Ancient Messene
Well-planned classical city in the southwestern Peloponnese. Date: 4th century BCE onwards. Contain city walls, public buildings, theaters, and sanctuaries. Offer unusually complete urban remains for study of classical city life.

Palace of Nestor
Bronze Age palace complex near Pylos. Date: Late Bronze Age (Mycenaean). Preserve Linear B tablet archives and well-laid rooms and storage areas. Provide key evidence of Mycenaean administration and economy.
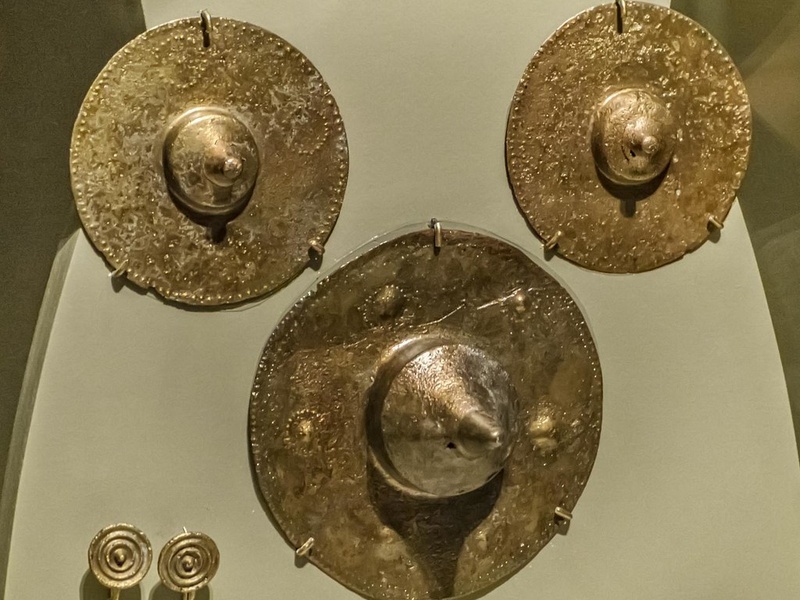

Vergina (Aigai)
Royal burial site in northern Greece. Date: Late Bronze Age and Classical periods. Contain richly furnished tombs, including a royal tomb attributed to Philip II. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status for archaeological significance.
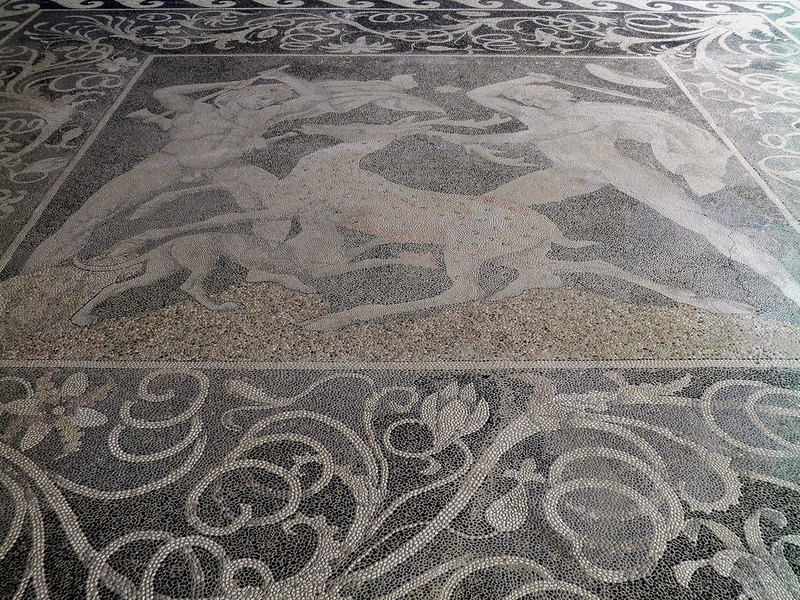

Pella
Capital of ancient Macedonia and birthplace of Alexander the Great. Date: Classical period. Feature palace complexes, mosaics, and city planning. Yield insight into Macedonian culture and urban life.
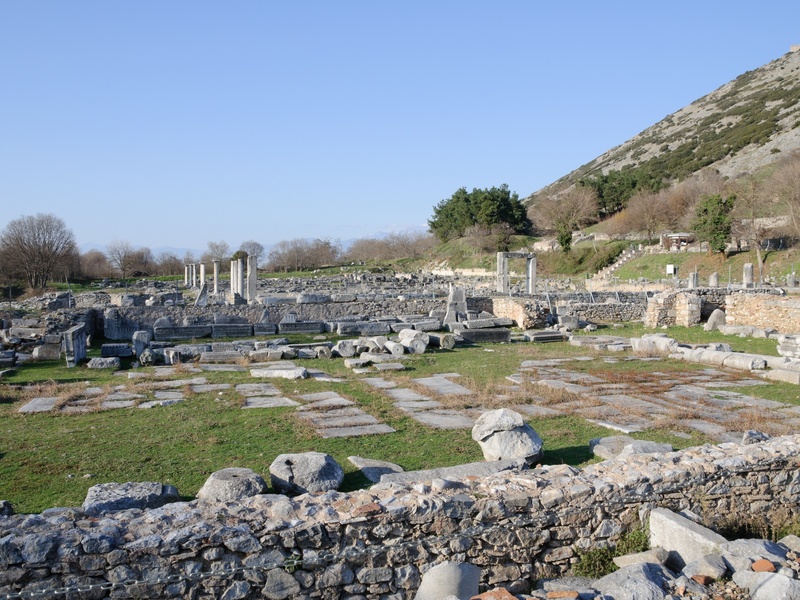

Philippi
Ancient city in eastern Macedonia with Hellenistic and Roman remains. Date: Hellenistic to Byzantine periods. Host a famous Roman colony, Christian basilicas, and battlefield history tied to Roman civil wars. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status as an archaeological site.
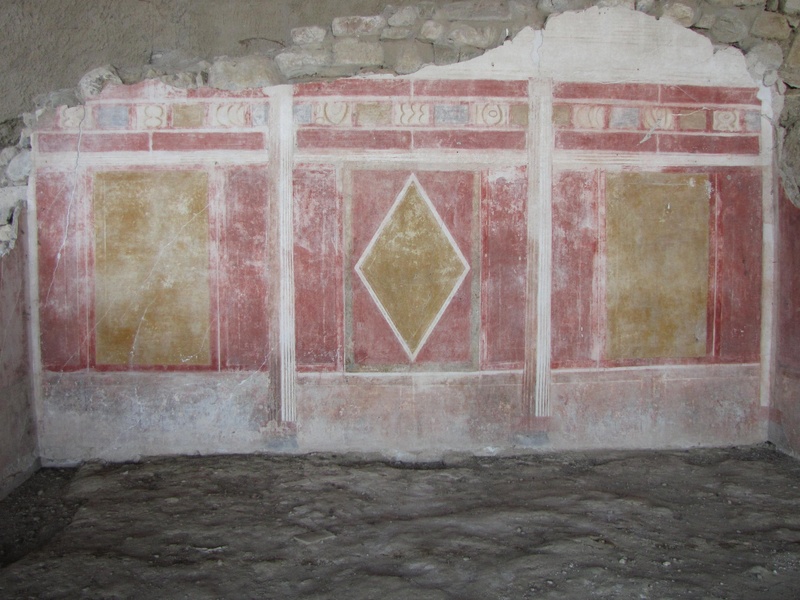

Amphipolis
Ancient city near the Strymon River in northern Greece. Date: Classical to Roman periods. Feature monumental tombs, a large bridge, and city walls. Offer evidence of Macedonian and Roman strategic interests.

Dion
Sanctuary and city at the foot of Mount Olympus. Date: Hellenistic and Roman periods. Combine religious sanctuaries, theaters, and baths. Reflect worship practices linked to Macedonian kings and mountain cults.
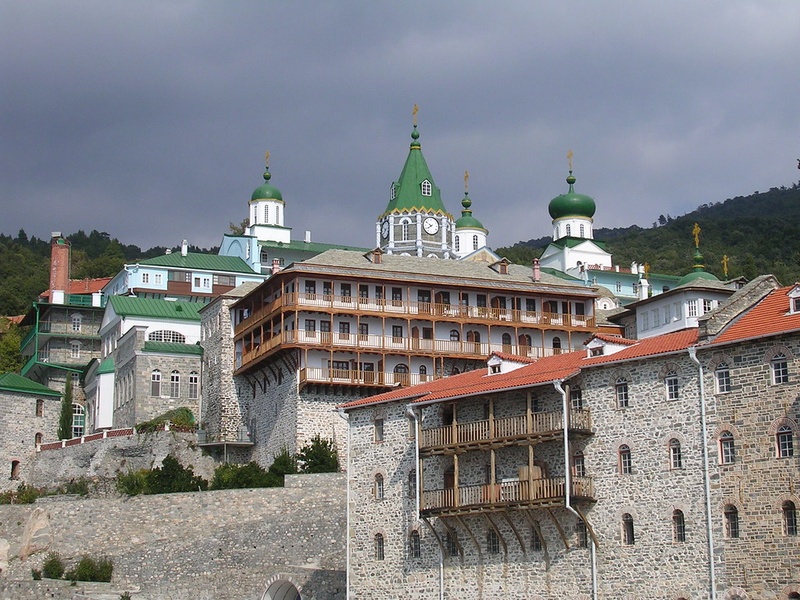

Mount Athos
Autonomous monastic peninsula in northern Greece. Date: Byzantine era to present. Host a cluster of active Orthodox monasteries with continuous monastic life. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status for cultural and spiritual heritage; access is restricted and male-only for entry.
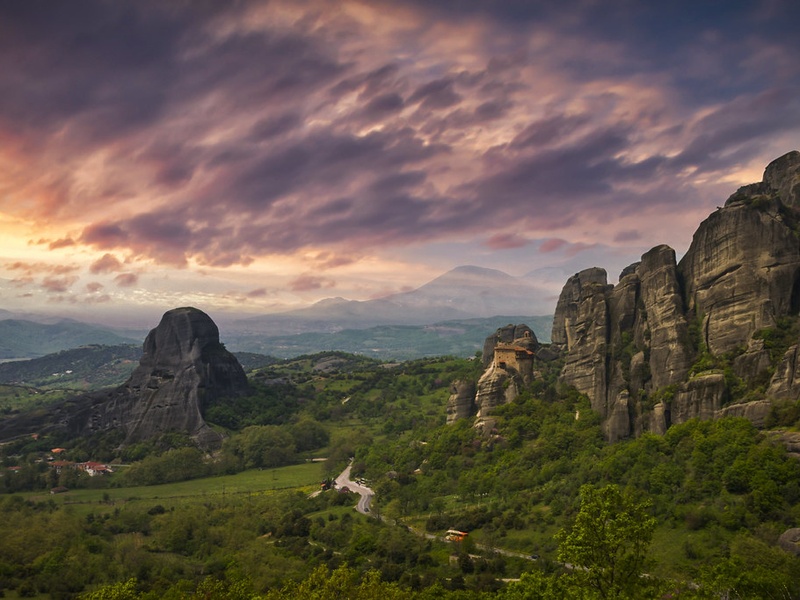

Meteora
Group of monasteries perched on sandstone pillars in central Greece. Date: Byzantine to Ottoman periods. Combine natural wonders with religious architecture. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status for cultural landscape and monastic tradition.
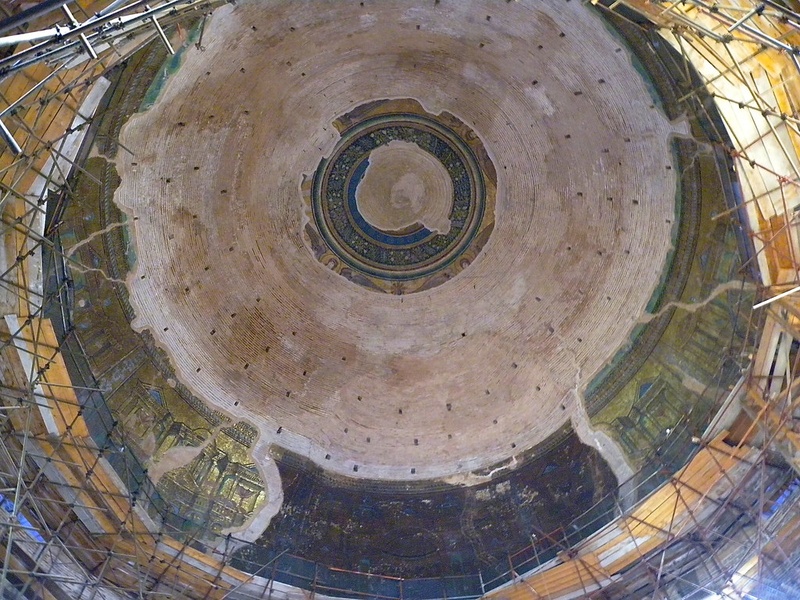

Thessaloniki Rotunda
Large circular Roman building in Thessaloniki. Date: early 4th century CE. Serve as a mausoleum, church, and mosque over time. Exhibit early Christian mosaics and Roman monumental architecture.
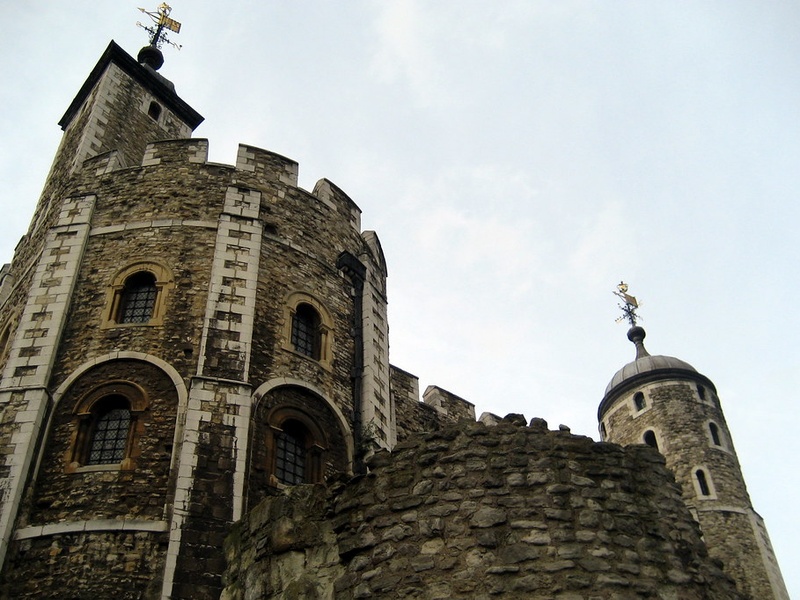

White Tower
20th-century landmark and former Ottoman fortress on Thessaloniki’s waterfront. Date: rebuilt in the 15th–16th centuries, modernized later. Symbolize Thessaloniki’s complex history and serve as a museum and city icon.
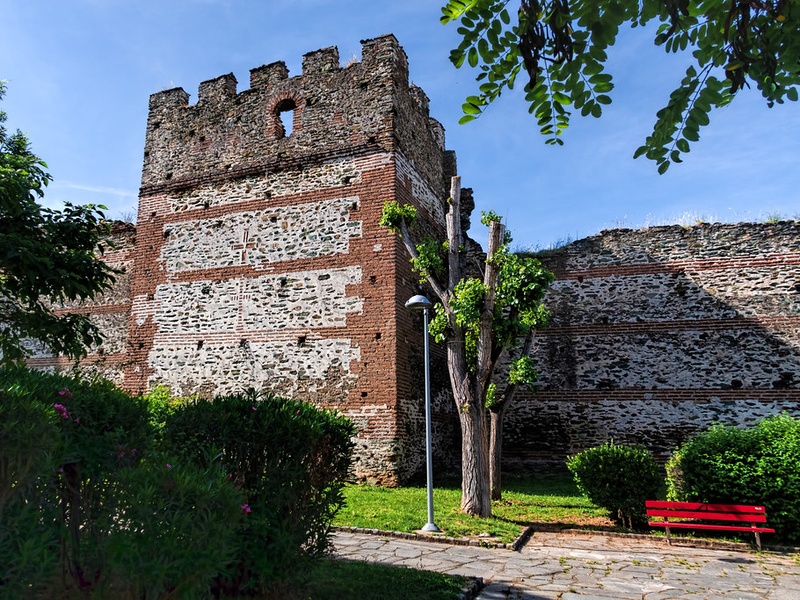

Byzantine Walls of Thessaloniki
Medieval city walls encircling Thessaloniki. Date: 4th–15th centuries with repairs over time. Provide urban defense and show Byzantine military architecture. Offer panoramic views and historical context for the city.
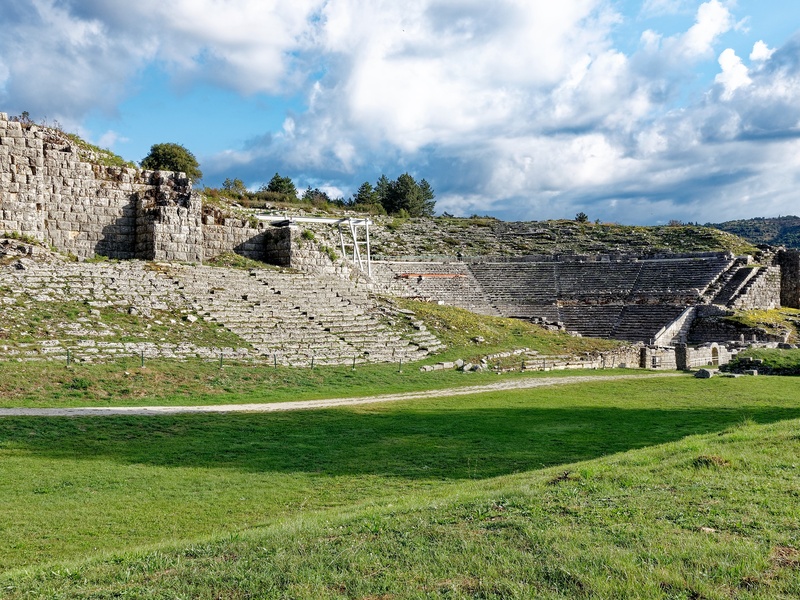

Dodona
Ancient oracle and sanctuary in Epirus. Date: Archaic and Classical periods. Host one of the oldest Greek oracles, linked to Zeus. Contain theater remains, temples, and sacred oak groves tied to divination.

Akrotiri (Thera)
Bronze Age settlement on Santorini preserved by volcanic ash. Date: Late Bronze Age (c.17th century BCE). Contain multi-story buildings, frescoes, and advanced urban planning. Provide key evidence of Aegean life and trade.
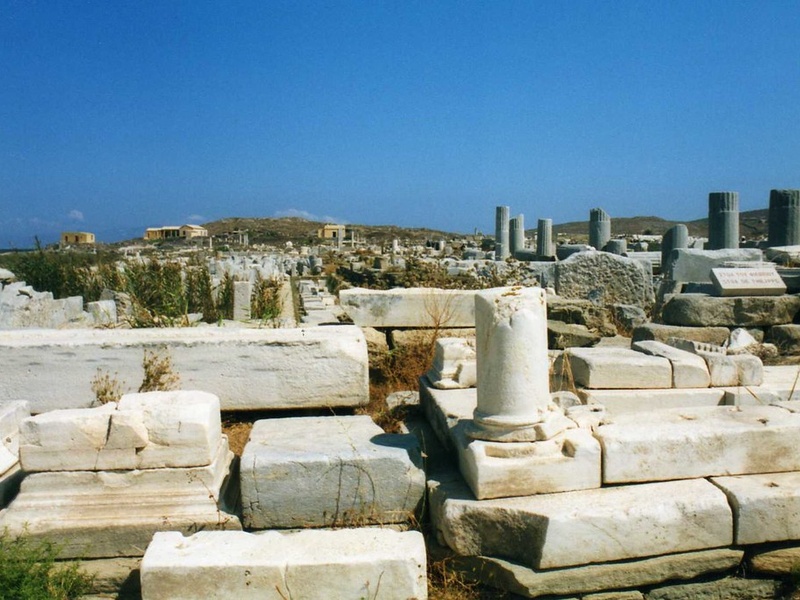

Delos
Sacred island near Mykonos and a major religious and commercial center. Date: Archaic through Roman periods. Honor Apollo and Artemis and host a vast archaeological site with sanctuaries, houses, and mosaics. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status.
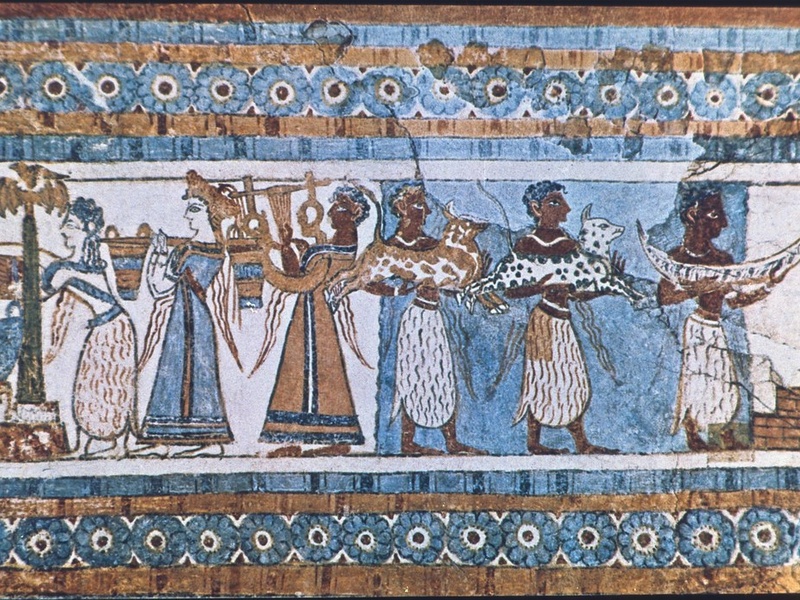

Knossos
Largest Minoan palace complex on Crete. Date: Bronze Age (c.2000–1400 BCE). Feature labyrinthine architecture, frescoes, and ceremonial spaces. Serve as the center of Minoan civilization and mythic associations like the Minotaur.
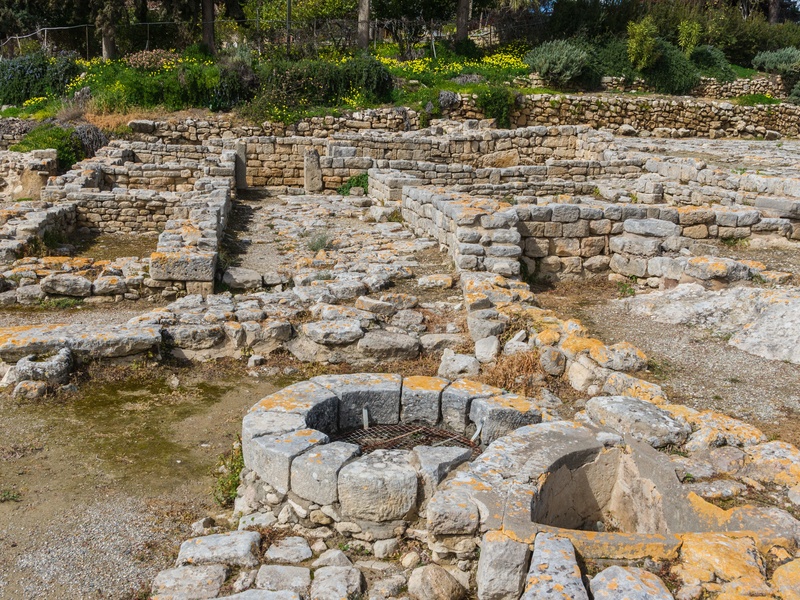

Phaistos
Major Minoan palace on southern Crete. Date: Bronze Age. Contain a large central courtyard, storage rooms, and the famous Phaistos Disc find. Offer insight into Minoan administration and ceremonial life.

Malia
Minoan palace and settlement on northern Crete. Date: Bronze Age. Present palace ruins, fortifications, and surrounding town remains. Help reconstruct Minoan social and economic networks.
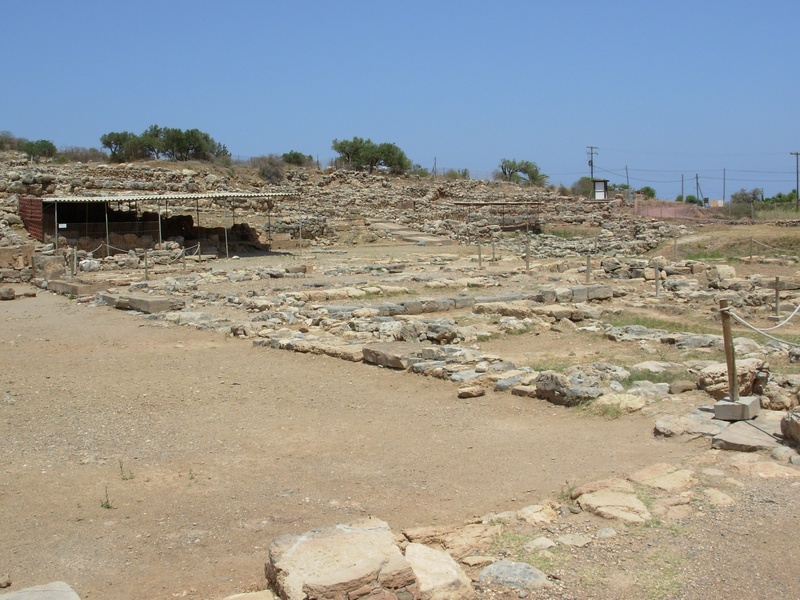

Zakros
Eastern Cretan Minoan palace and harbor site. Date: Bronze Age. Combine palace architecture with coastal trade evidence. Yield important artifacts and Linear A records.
Gortyna
Ancient city and Roman capital on southern Crete. Date: Classical to Roman periods. Contain law codes inscribed in stone, an odeon, and remains of Roman public buildings. Illustrate Roman provincial urban life.
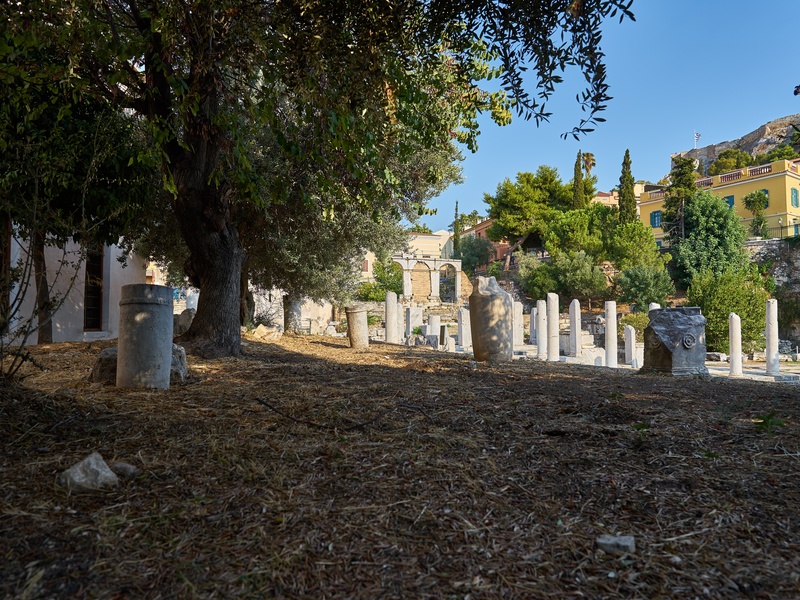

Roman Agora of Athens
Market complex built by Roman patrons in Athens. Date: 1st century BCE–1st century CE. Replace or complement the classical Agora with new structures and monuments. Show Roman influence on urban civic spaces.
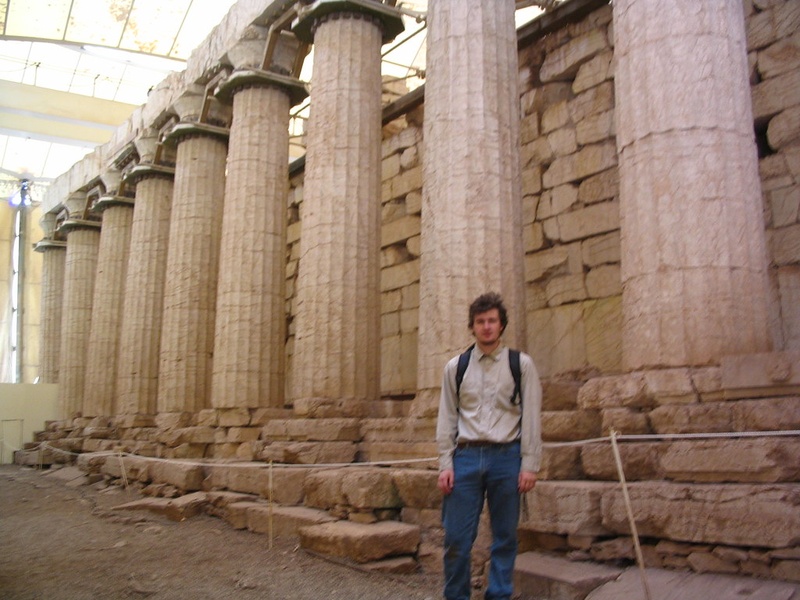

Temple of Apollo at Bassae
Well-preserved temple in the Peloponnese combining Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian orders. Date: 5th century BCE. Honor Apollo and demonstrate architectural innovation. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status as part of ancient Greek monuments.
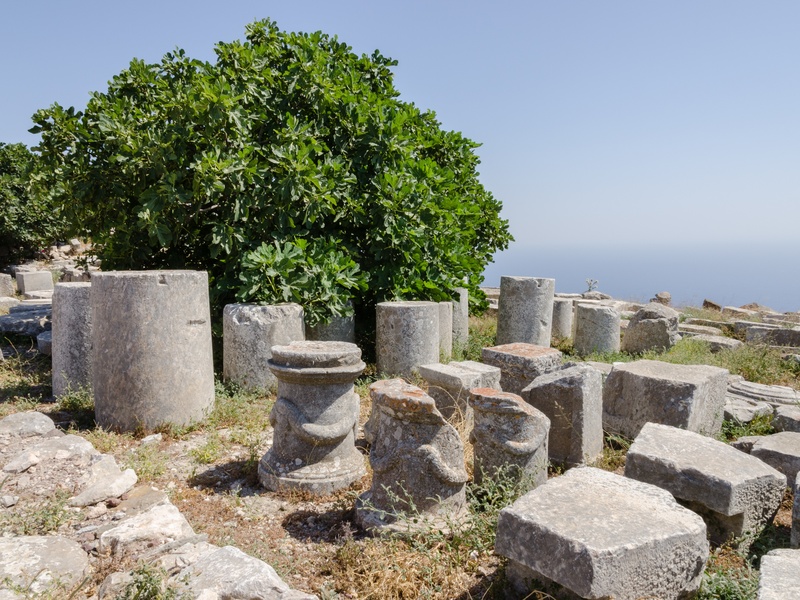

Ancient Thera
Hellenistic and Roman city on Santorini’s ridge. Date: Hellenistic to Byzantine periods. Contain urban streets, houses, and public buildings overlooking the sea. Show continuity of settlement across eras.
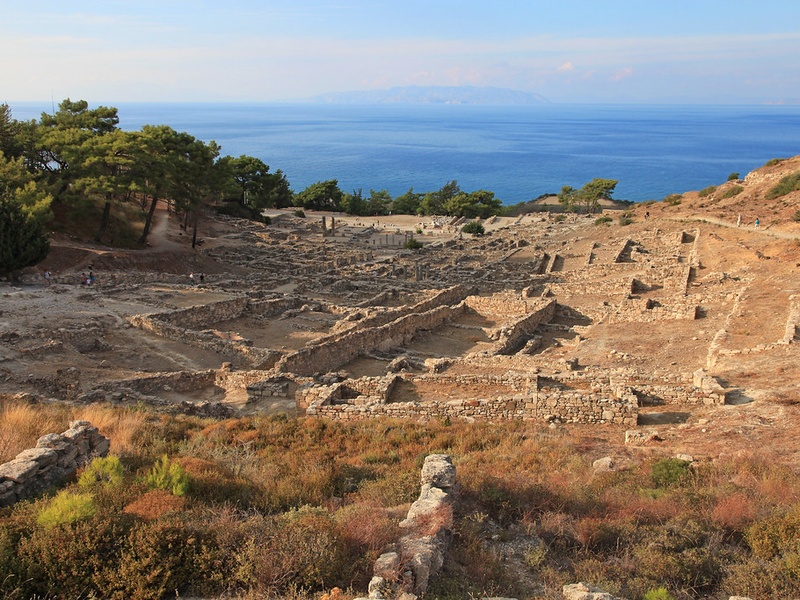

Kamiros
Ancient Doric city on the island of Rhodes. Date: Archaic to Hellenistic periods. Retain city planning, street grids, and public buildings. Provide a clear example of island urbanism and layout.
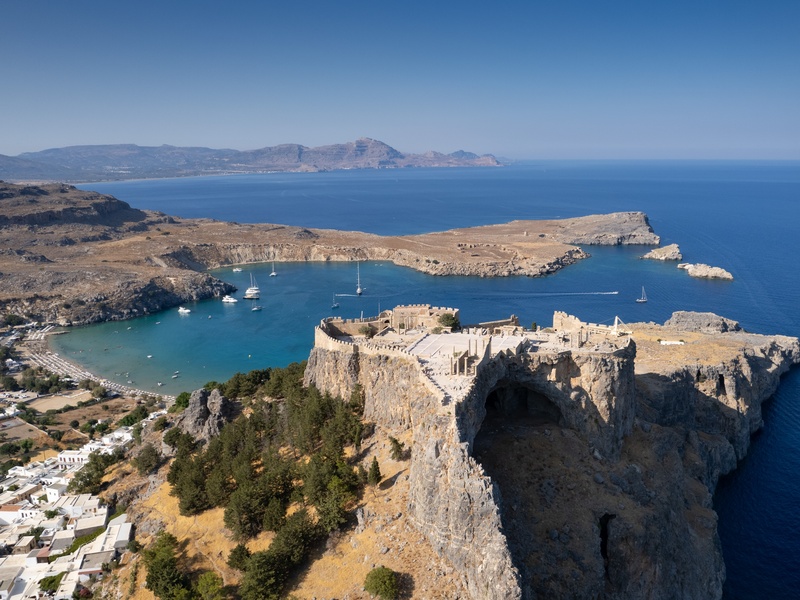

Lindos Acropolis
Acropolis on Rhodes with layered remains from Archaic to Medieval times. Date: Archaic through Byzantine periods. Feature a Doric temple, Hellenistic stoa, and Crusader castle. Combine religious significance with stunning coastal views.
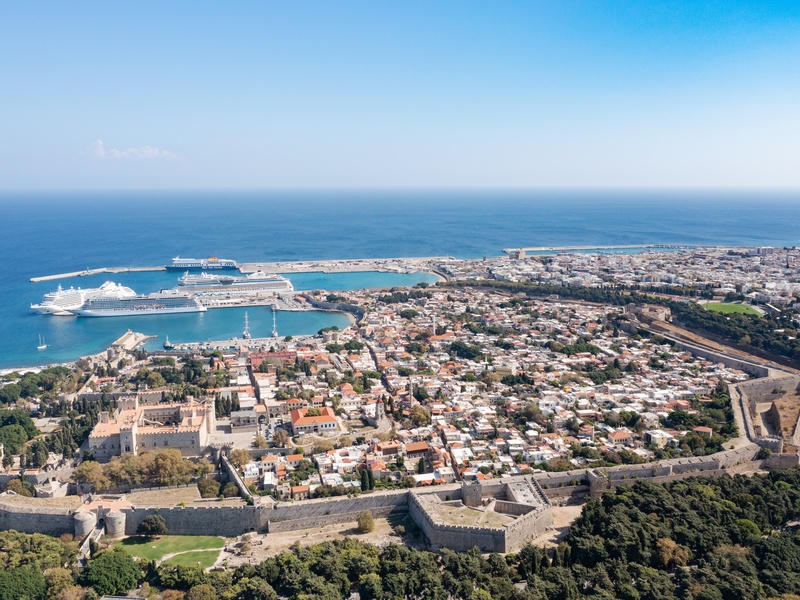

Rhodes Old Town
Medieval walled city and harbor center on Rhodes. Date: Hospitaller period and earlier. Contain Gothic palaces, narrow streets, and fortifications. Hold UNESCO World Heritage status for medieval architecture and historic urban fabric.
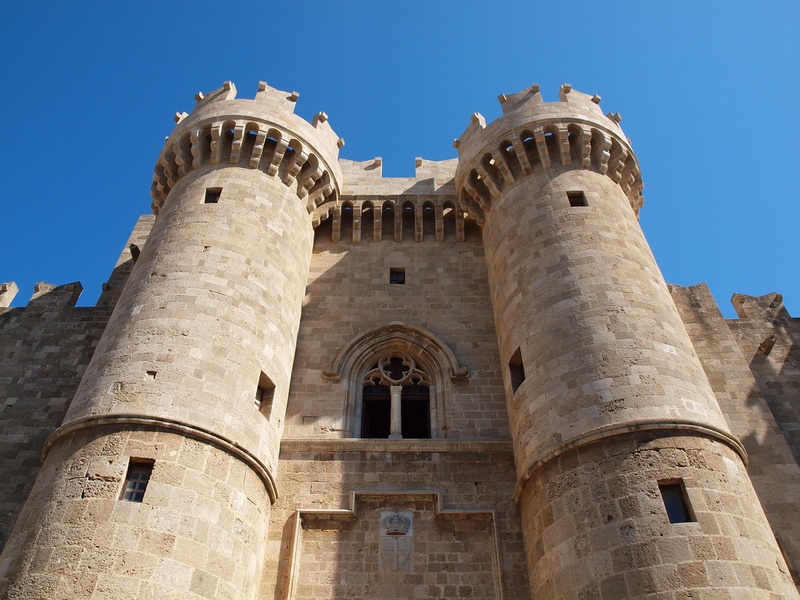

Palace of the Grand Master
Imposing Crusader-era fortress and palace in Rhodes Old Town. Date: 14th century with later restorations. Serve as the Knights Hospitaller administrative center and a clear example of medieval military architecture.

Ancient Sparta
Classical-era city-state center located in the Eurotas valley. Date: Archaic to Roman periods. Emphasize military discipline, unique social systems, and austere urban remains. Offer archaeological and literary evidence of Spartan society.

Ancient Theater of Mytilene
Hellenistic-Roman theater on Lesbos. Date: Hellenistic to Roman periods. Host dramatic and musical performances and show typical Greek theater design. Provide regional cultural context for the island.

Ancient Eretria
Archaeological site on the island of Euboea. Date: Geometric through Classical periods. Include sanctuaries, a theater, and fortifications. Reflect early Greek colonization and regional trade.

Thermopylae battlefield
Narrow coastal pass famous for ancient battles. Date: Classical era, notably 480 BCE. Mark a strategic chokepoint where Spartan-led forces held off Persian armies. Serve as a symbol of resistance and military history.

Plataea
Site of the decisive battle between Greek city-states and Persia. Date: 479 BCE. Host battlefield remains and memorials to the Greek victory. Represent cooperation among Greek poleis against external invasion.

Marathon
Plain northeast of Athens known for the 490 BCE battle. Date: Classical era. Mark the Athenians’ victory over Persian forces and inspire the modern marathon race. Preserve burial mounds and a battle memorial.
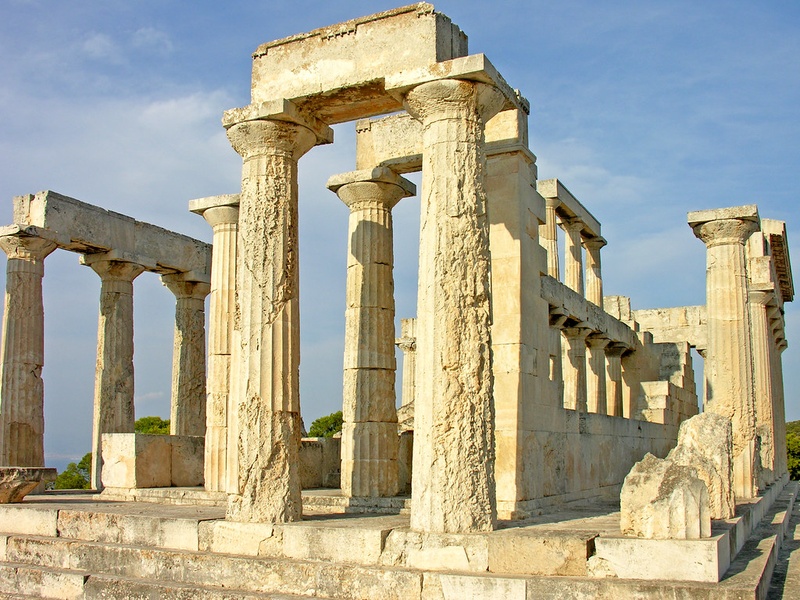

Temple of Aphaia
Archaic Doric temple on the island of Aegina. Date: c.500 BCE. Honor the local goddess Aphaia and form a visual triangle with the Parthenon and Poseidon temple at Sounion. Offer high-quality sculpture and a clear example of Archaic art.

Spinalonga
Fortress islet off Crete used as a Venetian stronghold and later a leper colony. Date: Venetian period and 1900s. Contain fortifications, housing ruins, and poignant social history. Illustrate shifting uses of island fortresses.
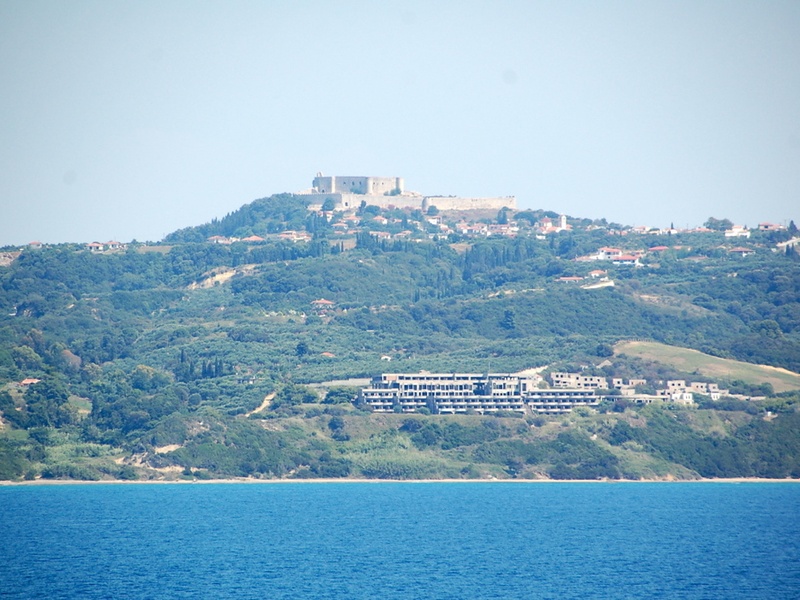

Chlemoutsi Castle
Frankish crusader castle in the Peloponnese. Date: early 13th century. Function as a strategic stronghold with massive keep and curtain walls. Provide an example of Western medieval architecture in Greece.
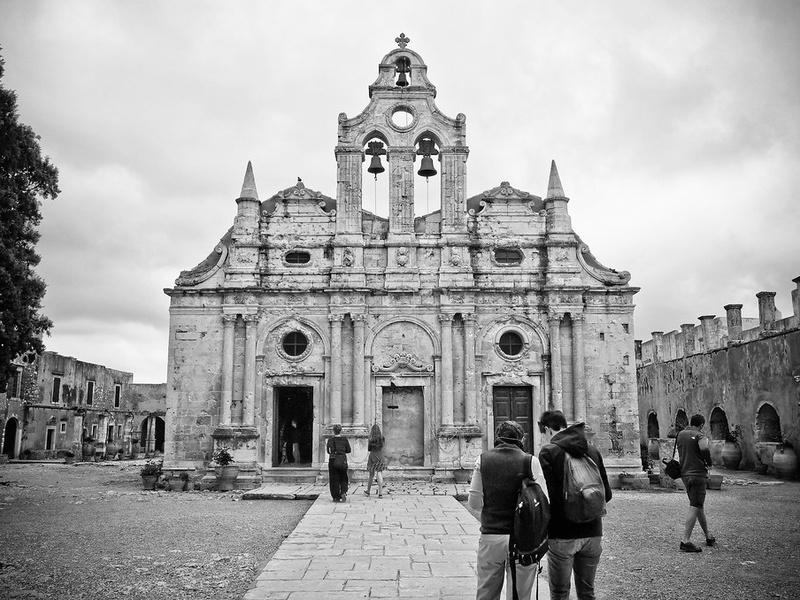

Arkadi Monastery
Cretan Orthodox monastery known for heroic resistance in 1866. Date: Byzantine foundation, Ottoman era significance. Serve as a national symbol of Cretan resistance and house notable frescoes and architecture.
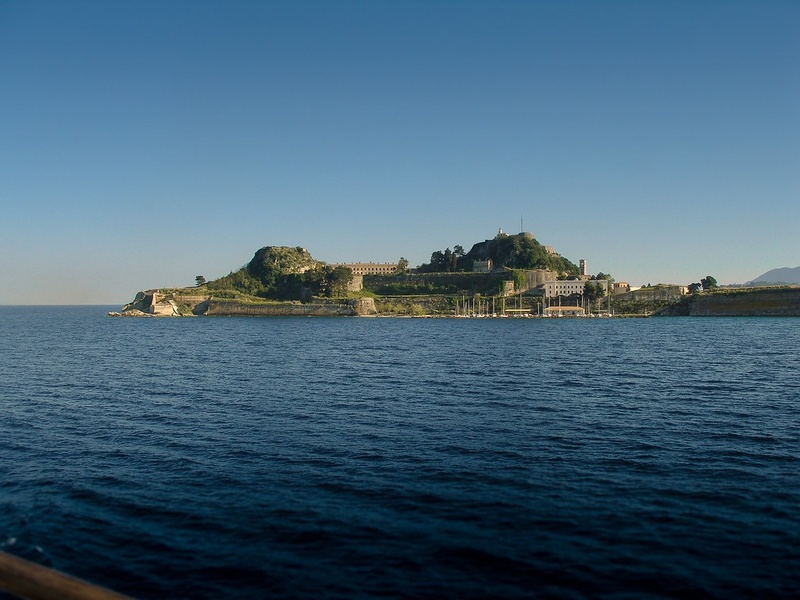

Corfu Old Fortress
Venetian-built fortress guarding Corfu town. Date: medieval to early modern periods. Overlook the harbor and contain layered defenses. Show Venetian military engineering and island strategic value.

Treasury of Atreus
Large Bronze Age beehive tomb near Mycenae. Date: Late Bronze Age. Contain a monumental corbelled dome and rich funerary architecture. Represent elite burial practices of the Mycenaean elite.

Franchthi Cave
Prehistoric cave in the Argolid with long occupation layers. Date: Paleolithic to Neolithic periods. Preserve evidence of early human settlement, tool use, and changing subsistence strategies in Greece.

Petralona Cave
Cave in northern Greece with early human fossils. Date: Pleistocene era. Contain hominin remains and prehistoric tools that inform human evolution in the Balkans. Serve as an important paleoanthropological site.
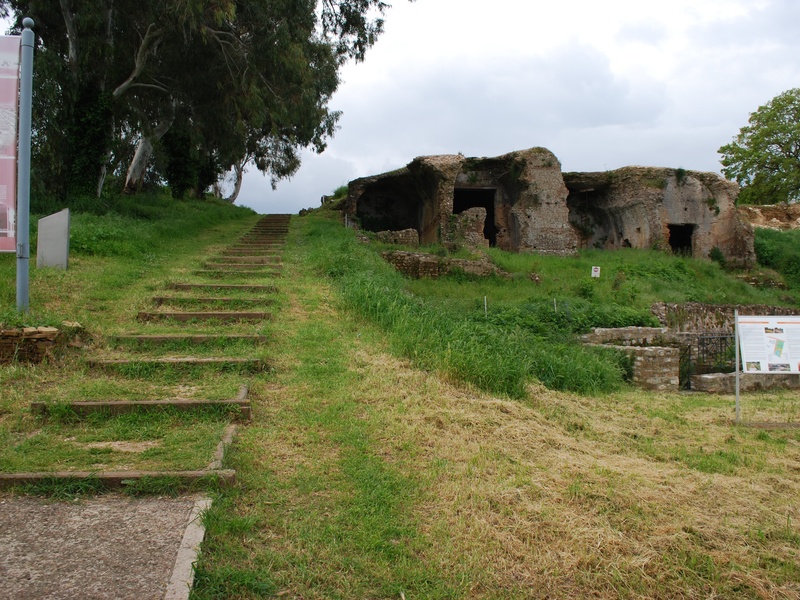

Nicopolis
Roman city founded by Octavian near Actium. Date: Roman period. Function as a memorial and urban center with theater, baths, and basilicas. Reflect Roman urbanism and imperial commemoration.
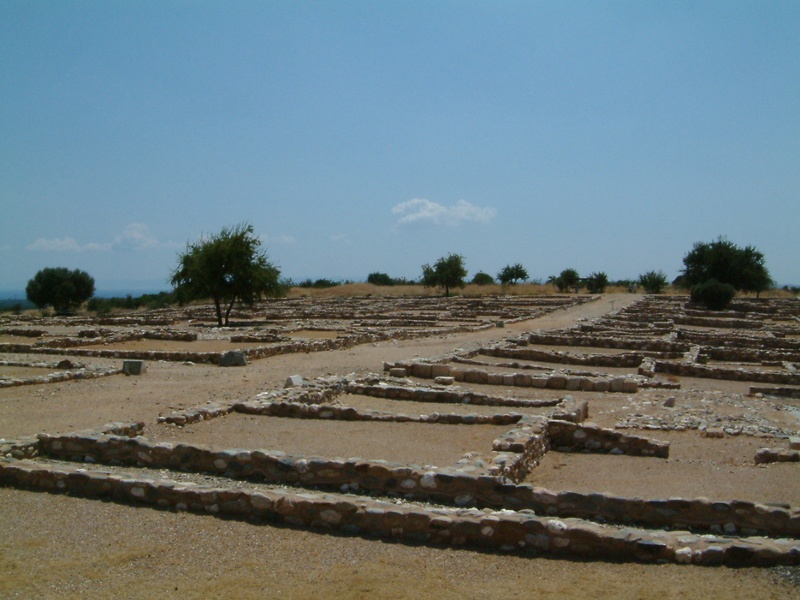

Olynthos
Planned Classical city in Halkidiki. Date: Classical period. Exhibit orthogonal street grids and house plans with mosaic floors. Provide valuable evidence of domestic life and urban planning.
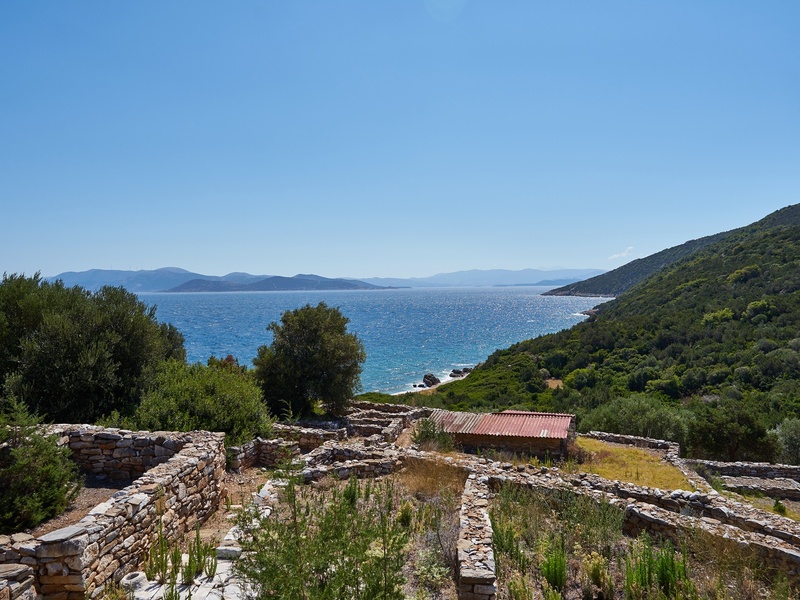

Rhamnous
Coastal sanctuary and fortress northeast of Athens. Date: Archaic to Classical periods. Honor Nemesis and contain a well-preserved temple and fortification remains. Offer insight into regional cults and maritime defense.

Helike
Ancient city that sank in a catastrophic earthquake and tsunami. Date: Classical era. Present a case of sudden urban destruction and mythic memory. Under archaeological investigation with potential submerged remains.






